Home > Press > DNA origami to scale-up molecular motors
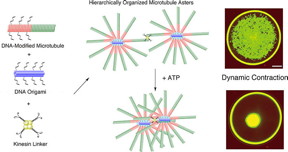 |
| Mixing DNA-modified microtubules, DNA origami and kinesin linkers leads to star-like formations of microtubules that are connected by kinesin linkers. This network contracted dynamically when ATP energy was added. (Matsuda K. et al., Nano Letters, April 30, 2019) |
Abstract:
Researchers have successfully used DNA origami to make smooth-muscle-like contractions in large networks of molecular motor systems, a discovery which could be applied in molecular robotics.
DNA origami to scale-up molecular motors
Tokyo, Japan | Posted on June 13th, 2019"We successfully demonstrated programmed self-assembly of a biomolecular motor system," write the researchers from Japan and Germany who conducted the study.
The biomolecular motor system, consisting of fibrous microtubules and motor protein kinesins, plays an essential role in cellular transportation systems. Scientists believe they can utilize the motors in molecular robotics but it remains difficult to assemble a larger system from the tiny molecules.
In the current study published in Nano Letters, the research team including Akira Kakugo of Hokkaido University, Akinori Kuzuya of Kansai University, and Akihiko Konagaya of Tokyo Institute of Technology developed a system combining DNA origami and microtubules. The DNA origami were formed from six DNA helices bundled together. Mixing the two components caused the microtubules to self-assemble around the DNA origami forming star-shaped structures. This self-assembly was made possible by the binding of complementary DNA strands attached to each component.
The team then designed a "kinesin linker" which is made of four kinesin motor proteins radiating from a central core protein. These kinesin linkers joined the microtubules together, causing multiple star-like assemblies to connect, forming a much larger hierarchical network.
When adenosine triphosphate (ATP), a molecule which stores and carries energy, was added to the system, the kinesin linkers moved, causing the microtubular network to dynamically contract within a matter of minutes. This resembled the contraction of smooth muscles according to the researchers.
This dynamic contraction only happened when the DNA origami were present, suggesting the importance of the hierarchical assembly within the microtubular network. "Further studies could lead to the use of DNA for controlled, programmable self-assembly and contraction of biomolecular motors. Such motors could find applications in molecular robotics and the development of microvalves for microfluidic devices," says Akira Kakugo.
Reference
Authors :
Kento Matsuda1, Arif Md. Rashedul Kabir2, Naohide Akamatsu3, Ai Saito1, Shumpei Ishikawa3, Tsuyoshi Matsuyama3, Oliver Ditzer4, Md. Sirajul Islam5, Yuichi Ohya3,5, Kazuki Sada1,2, Akihiko Konagaya6, Akinori Kuzuya3,5,*, and Akira Kakugo1,2,*
Title of original paper :
Artificial Smooth Muscle Model Composed of Hierarchically Ordered Microtubule Asters Mediated by DNA Origami Nanostructures.
Journal :
Nano Letters
DOI :
10.1021/acs.nanolett.9b01201 outer
Affiliations :
1Graduate School of Chemical Sciences and Engineering, Hokkaido University
2Faculty of Science, Hokkaido University
3Department of Chemistry and Materials Engineering, Kansai University
4Faculty of Chemistry and Food Chemistry, Technische Universität Dresden
5Organization for Research and Development of Innovative Science and Technology, Kansai University
6Department of Computational Intelligence and Systems Science, Tokyo Institute of Technology
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Further Information
Professor Akihiko Konagaya
School of Computing, Tokyo Institute of Technology
Email
Tel +81-45-924-5655
Contact
Public Relations Section, Tokyo Institute of Technology
Email
Tel +81-3-5734-2975
*Corresponding authors' email:
Copyright © Tokyo Institute of Technology
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Videos/Movies
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Robotics
![]() Nanofibrous metal oxide semiconductor for sensory face November 8th, 2024
Nanofibrous metal oxide semiconductor for sensory face November 8th, 2024
![]() Femtosecond laser technique births "dancing microrobots": USTC's breakthrough in multi-material microfabrication August 11th, 2023
Femtosecond laser technique births "dancing microrobots": USTC's breakthrough in multi-material microfabrication August 11th, 2023
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Molecular Machines
![]() First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
![]() Nanotech scientists create world's smallest origami bird March 17th, 2021
Nanotech scientists create world's smallest origami bird March 17th, 2021
![]() Giant nanomachine aids the immune system: Theoretical chemistry August 28th, 2020
Giant nanomachine aids the immune system: Theoretical chemistry August 28th, 2020
Molecular Nanotechnology
![]() Quantum pumping in molecular junctions August 16th, 2024
Quantum pumping in molecular junctions August 16th, 2024
![]() Scientists push the boundaries of manipulating light at the submicroscopic level March 3rd, 2023
Scientists push the boundaries of manipulating light at the submicroscopic level March 3rd, 2023
![]() First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
Self Assembly
![]() Diamond glitter: A play of colors with artificial DNA crystals May 17th, 2024
Diamond glitter: A play of colors with artificial DNA crystals May 17th, 2024
![]() Liquid crystal templated chiral nanomaterials October 14th, 2022
Liquid crystal templated chiral nanomaterials October 14th, 2022
![]() Nanoclusters self-organize into centimeter-scale hierarchical assemblies April 22nd, 2022
Nanoclusters self-organize into centimeter-scale hierarchical assemblies April 22nd, 2022
![]() Atom by atom: building precise smaller nanoparticles with templates March 4th, 2022
Atom by atom: building precise smaller nanoparticles with templates March 4th, 2022
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








