Home > Press > Atom by atom: building precise smaller nanoparticles with templates
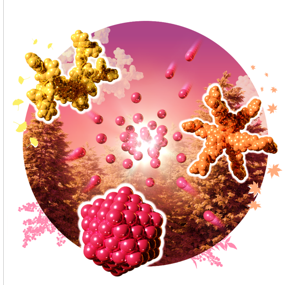 |
| This scientific illustration of the study, created by Dr Takamasa Tsukamoto of Tokyo Tech, was selected as an Inside Cover Picture in Angewandte Chemie International Edition. Image source: Dr. Tsukamoto, Tokyo Tech CREDIT Dr Takamasa Tsukamoto of Tokyo Tech |
Abstract:
Nanoparticles (which have sizes ranging between 3–500 nm), and sub-nanoclusters (which are around 1 nm in diameter) are utilized in many fields, including medicine, robotics, materials science, and engineering. Their small size and large surface-area-to-volume ratios give them unique properties, rendering them valuable in a variety of applications, ranging from pollution control to chemical synthesis.
Atom by atom: building precise smaller nanoparticles with templates
Tokyo, Japan | Posted on March 4th, 2022Recently, quasi-sub-nanomaterials, which are about 1-3 nm in scale have attracted attention because they have a dual nature–they can be regarded as nanoparticles, as well as inorganic molecules. Understandably, controlling the number of atoms in a quasi-sub-nanomaterial could be of much value. However, synthesizing such precise molecular structures is technically challenging–but scientists at Tokyo Tech were certainly up for this challenge!
Dendrons – highly branched molecular structures consisting of basic imines – have been suggested as precursors for the precise synthesis of quasi-sub-nanomaterials with the desired number of atoms. The imines in the dendrons function as a scaffold that can form complexes with certain acidic metallic salts, accumulating metals on the dendron structure. These, in turn, can be reduced to metal sub-nanoclusters with the desired number of atoms. However, synthesizing dendrons with a high proportion of imines is an expensive process with low yield.
Now, in a study published in Angewandte Chemie, the researchers explain how they have combined multiple dendrimer structures to form a supramolecular capsule composed of more than 60 imines. “The synthesis of dendron-assembled supramolecules was accomplished by connecting internal core units and external dendron units—which determine the central structure and terminal branches, respectively,” explains Assistant Professor Takamasa Tsukamoto, who was involved in the study. The internal structure of this supramolecule contained a six-pronged core with acidic tritylium, while each outer unit contained dendrons with imines. The interaction between the acidic core and the basic outer structure resulted in a self-assembling organo-complex.
Moreover, the imines were found to co-accumulate with rhodium salts such that the innermost imines formed a complex with tritylium units while the outermost ones were populated with the rhodium salts. The resulting supramolecule, which had an internal core unit surrounded by six external dendron units (each containing 14 rhodium salts at the outer imines), was successfully condensed to clusters containing 84 rhodium atoms having a size of 1.5 nm.
By attaching imine containing dendrons to an acidic core, the researchers constructed a supramolecular template for the synthesis of quasi-sub-nanomaterials. Moreover, since the imines can form complexes with a wide range of cationic units, the method can be used to synthesize a variety of supramolecular structures. Due to its versatility, simplicity and cost-effectiveness, the method can be a cornerstone for the development of new nanomaterials. “This novel approach for obtaining atomicity-defined quasi-sub-nanomaterials without the limitations of conventional methods has the potential to play an important role in exploring the last frontiers of nanomaterials,” says Prof. Tsukamoto. Indeed, this may be a “small” step for Tokyo Tech, but a “giant” step for nanoscience!
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Kazuhide Hsegawa
Tokyo Institute of Technology
Copyright © Tokyo Institute of Technology
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanofabrication
![]() Self-propelled protein-based nanomotors for enhanced cancer therapy by inducing ferroptosis June 6th, 2025
Self-propelled protein-based nanomotors for enhanced cancer therapy by inducing ferroptosis June 6th, 2025
![]() Multiphoton polymerization: A promising technology for precision medicine February 28th, 2025
Multiphoton polymerization: A promising technology for precision medicine February 28th, 2025
![]() New chip opens door to AI computing at light speed February 16th, 2024
New chip opens door to AI computing at light speed February 16th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Self Assembly
![]() Diamond glitter: A play of colors with artificial DNA crystals May 17th, 2024
Diamond glitter: A play of colors with artificial DNA crystals May 17th, 2024
![]() Liquid crystal templated chiral nanomaterials October 14th, 2022
Liquid crystal templated chiral nanomaterials October 14th, 2022
![]() Nanoclusters self-organize into centimeter-scale hierarchical assemblies April 22nd, 2022
Nanoclusters self-organize into centimeter-scale hierarchical assemblies April 22nd, 2022
![]() Nanostructures get complex with electron equivalents: Nanoparticles of two different sizes break away from symmetrical designs January 14th, 2022
Nanostructures get complex with electron equivalents: Nanoparticles of two different sizes break away from symmetrical designs January 14th, 2022
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








