Home > Press > The mechanism of a novel circular RNA circZFR that promotes colorectal cancer progression
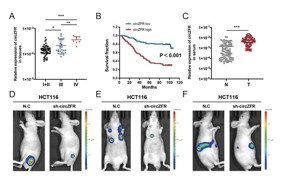 |
| The level of circZFR is associated with CRC stage and survival, and circZFR promotes CRC growth and metastasis in vivo CREDIT ©Science China Press |
Abstract:
This study is reported by Zhangfa Song’s group from the Sir Run Run Shaw Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine. The research team identified circZFR using circRNA microarray and competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) microarray, and they confirmed that circZFR is a promising biomarker for CRC diagnosis and prognosis. Currently, the morbidity and mortality of CRC remain high due to the lack of early symptoms and effective early screening technology. Metastasis and recurrence remain the most common causes of death related to CRC. Therefore, it is crucial to find novel biomarkers for CRC diagnosis and prognosis, as well as unravel their mechanisms of action.
The mechanism of a novel circular RNA circZFR that promotes colorectal cancer progression
Beijing, China | Posted on July 5th, 2024The team studied the function of circZFR, as well as the upstream and downstream events that promote CRC progression. Highly expressed circZFR promotes the proliferation and migration of CRC cells directly or via exosomes. In mouse models, circZFR stimulates tumor growth, and lung and liver metastasis. Mechanistically, ESRP1 in CRC cells may enhance the production of circZFR. The oncogenic protein BCLAF1 binds to circZFR, preventing the ubiquitinated degradation of BCLAF1. In addition, circZFR sponges miR-3127-5p to boost RTKN2 expression. These findings support the use of circZFR as a potential biomarker for CRC diagnosis and a desirable target for future treatment.
The study further shows that the TCP1-CD-QDs nanocarrier is able to carry and deliver circZFR siRNA (si-circZFR) to the vasculature of CRC tissues, effectively inhibiting tumor growth. “The unique looping structure of circRNAs renders them extremely stable, implying that these molecules have a strong biomarker potential for early screening, diagnosis, and prognosis. Our study on circZFR will provide help for researchers in this field to explore more novel functional circRNAs”. Zhangfa Song – the lead author of the study – noted.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Media Contact
Bei Yan
Science China Press
Expert Contact
Zhangfa Song
Sir Run Run Shaw Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou, China
Copyright © Science China Press
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Cancer
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Self-propelled protein-based nanomotors for enhanced cancer therapy by inducing ferroptosis June 6th, 2025
Self-propelled protein-based nanomotors for enhanced cancer therapy by inducing ferroptosis June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








