Home > Press > Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies
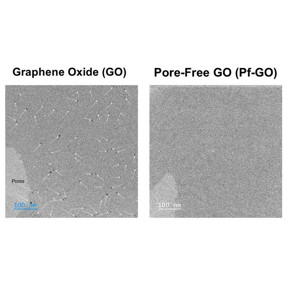 |
| Numerous pores were observed in GO (indicated by white arrows). In contrast, no pores were visible in Pf-GO, even under high magnification. Credit Kazuto Hatakeyama and Shintaro Ida from Kumamoto University |
Abstract:
Kumamoto University’s research team, led by Assistant Professor Kazuto Hatakeyama and Professor Shintaro Ida of Institute of Industrial Nanomaterials, has announced a groundbreaking development in hydrogen ion barrier films using graphene oxide (GO) that lacks internal pores. This innovative approach promises significant advancements in protective coatings for various applications.
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies
Kumamoto, Japan | Posted on September 13th, 2024In their study, the research team successfully synthesized and developed a thin film from a new form of graphene oxide that does not contain pores. Traditionally, GO has been known for its high ionic conductivity, which made it challenging to use as an ion barrier. However, by eliminating the internal pores, the team created a material with dramatically improved hydrogen ion barrier properties.
The new graphene oxide film exhibits up to 100,000 times better hydrogen ion barrier performance compared to conventional GO films, based on the AC impedance spectroscopy ‘s out-of-plane proton conductivity result. This breakthrough has also been demonstrated through experiments where the non-porous graphene oxide coating effectively protected lithium foil from water droplets, preventing any reaction between the lithium and the water.
The study also confirmed that hydrogen ions move through the pores in conventional GO, highlighting the significance of eliminating these pores to enhance barrier capabilities. This advancement opens doors to new applications in protective coatings, rust prevention, and hydrogen infrastructure.
This research marks a significant advance in materials science and could pave the way for next-generation coatings with enhanced protective properties. "Moving forward, we plan to harness the hydrogen ion barrier performance for practical applications, while also addressing the challenges posed by the 'pores' in the GO structure to unlock additional functionalities," explained Assistant Professor Hatakeyama as he outlined the next steps in his research.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Kumamoto University
Office: 96-342-3307
Copyright © Kumamoto University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
Coatings
![]() Closing the gaps — MXene-coating filters can enhance performance and reusability February 28th, 2025
Closing the gaps — MXene-coating filters can enhance performance and reusability February 28th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








