Home > Press > Ames Laboratory scientists move graphene closer to transistor applications
 |
Abstract:
Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy's Ames Laboratory were able to successfully manipulate the electronic structure of graphene, which may enable the fabrication of graphene transistors-- faster and more reliable than existing silicon-based transistors.
Ames Laboratory scientists move graphene closer to transistor applications
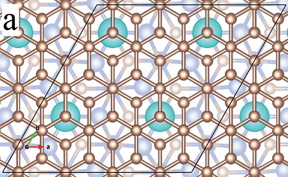
Ames, IA | Posted on August 30th, 2017The researchers were able to theoretically calculate the mechanism by which graphene's electronic band structure could be modified with metal atoms. The work will guide experimentally the use of the effect in layers of graphene with rare-earth metal ions "sandwiched" (or intercalated) between graphene and its silicon carbide substrate. Because the metal atoms are magnetic the additions can also modify the use of graphene for spintronics.
"We are discovering new and more useful versions of graphene," said Ames Laboratory senior scientist Michael C. Tringides. "We found that the placement of the rare earth metals below graphene, and precisely where they are located, in the layers between graphene and its substrate, is critical to manipulating the bands and tune the band gap."
Graphene, a two-dimensional layer of carbon, has been extensively studied by researchers everywhere since it was first produced in 2004 because electrons travel much faster along its surface, making it an ideal potential material for future electronic technologies. But the inability to control or tune graphene's unique properties has been an obstacle to its application.
Density Functional Theory calculations predicted the configurations necessary to demonstrate control of the band gap structure. "Ames Laboratory is very good at synthesis of materials, and we use theory to precisely determine how to modify the metal atoms," said Minsung Kim, a postdoctoral research associate. "Our calculations guided the placement so that we can manipulate these quantum properties to behave the way we want them to."
###
The work was supported by the U.S. Department of Department of Energy's Office of Science. Computations were performed through the support of the National Energy Research Scientific Computing Center (NERSC), a DOE Office of Science User Facility at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory.
####
About Ames Laboratory
Ames Laboratory is a U.S. Department of Energy Office of Science national laboratory operated by Iowa State University. Ames Laboratory creates innovative materials, technologies and energy solutions. We use our expertise, unique capabilities and interdisciplinary collaborations to solve global problems.
DOE's Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States, and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit science.energy.gov.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Laura Millsaps
Copyright © Ames Laboratory
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Hardware
![]() The present and future of computing get a boost from new research July 21st, 2023
The present and future of computing get a boost from new research July 21st, 2023
![]() A Carbon Nanotube Microprocessor Mature Enough to Say Hello: Three new breakthroughs make commercial nanotube processors possible March 2nd, 2020
A Carbon Nanotube Microprocessor Mature Enough to Say Hello: Three new breakthroughs make commercial nanotube processors possible March 2nd, 2020
![]() Powering the future: Smallest all-digital circuit opens doors to 5 nm next-gen semiconductor February 11th, 2020
Powering the future: Smallest all-digital circuit opens doors to 5 nm next-gen semiconductor February 11th, 2020
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Nanoelectronics
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
![]() Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
![]() Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








