Home > Press > Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices
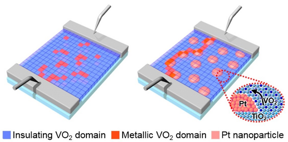 |
| Schematic of the effect of the “stepping-stone” current flow formed via the platinum nanoparticles inserted in the thin phase-transition oxide film CREDIT POSTECH |
Abstract:
Stepping stones are placed to help travelers to cross streams. As long as there are stepping stones that connect the both sides of the water, one can easily get across with just a few steps. Using the same principal, a research team at POSTECH has developed technology that cuts the power consumption in semiconductor devices in half by placing stepping stones.
Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices
Pohang, Korea | Posted on September 23rd, 2022A research team led by Professor Junwoo Son and Dr. Minguk Cho (Department of Materials Science and Engineering) at POSTECH has succeeded in maximizing the switching efficiency of oxide semiconductor devices by inserting platinum nanoparticles. The findings from the study were recently published in the international journal Nature Communications.
The oxide material with the metal-insulator phase transition, in which the phase of a material rapidly changes from an insulator to a metal when the threshold voltage is reached, is spotlighted as a key material for fabricating low-power semiconductor devices.
The metal–insulator phase transition occurs when insulator domains, several nanometer (nm, billionth of a meter) units big, are transformed into metal domains. The key was to reduce the magnitude of the voltage applied to the device to increase the switching efficiency of a semiconductor device.
The research team succeeded in increasing the switching efficiency of the device by using platinum nanoparticles. When voltage was applied to a device, an electric current “skipped” through these particles and a rapid phase transition occurred.
The memory effect of the device also increased by more than a million times. In general, after the voltage is cut off, it immediately changes to the insulator phase where no current flows; this duration was extremely short at 1 millionth of a second. However, it was confirmed that the memory effect of remembering the previous firing of the devices can be increased to several seconds, and the device could be operated again with relatively low voltage owing to the residual metallic domains remaining near the platinum nanoparticles.
This technology is anticipated to be essential for the development of next-generation electronic devices, such as intelligent semiconductors or neuromorphic semiconductor devices that can process vast amounts of data with less power.
This study was conducted with the support from the Basic Science Research Program, Mid-career Researcher Program, and the Next-generation Intelligence Semiconductor Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Jinyoung Huh
Pohang University of Science & Technology (POSTECH)
Office: 82-54-279-2415
Copyright © Pohang University of Science & Technology (POSTECH)
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Nanoelectronics
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
![]() Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
![]() Atomic level deposition to extend Moore’s law and beyond July 15th, 2022
Atomic level deposition to extend Moore’s law and beyond July 15th, 2022
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








