Home > Press > Using light to propel water : With new method, MIT engineers can control and separate fluids on a surface using only visible light
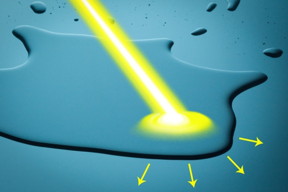 |
| A new system developed by MIT engineers could make it possible to control the way water moves over a surface, using only light. Image: Jose-Luis Olivares/MIT |
Abstract:
A new system developed by engineers at MIT could make it possible to control the way water moves over a surface, using only light. This advance may open the door to technologies such as microfluidic diagnostic devices whose channels and valves could be reprogrammed on the fly, or field systems that could separate water from oil at a drilling rig, the researchers say.
Using light to propel water : With new method, MIT engineers can control and separate fluids on a surface using only visible light
Cambridge, MA | Posted on April 25th, 2017The system, reported in the journal Nature Communications, was developed by MIT associate professor of mechanical engineering Kripa Varanasi, School of Engineering Professor of Teaching Innovation Gareth McKinley, former postdoc Gibum Kwon, graduate student Divya Panchanathan, former research scientist Seyed Mahmoudi, and Mohammed Gondal at the King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals in Saudi Arabia.
The initial goal of the project was to find ways of separating oil from water, for example, to treat the frothy mixture of briny water and crude oil produced from certain oil wells. The more thoroughly these mixtures are intermingled — the finer the droplets are — the harder they are to separate. Sometimes electrostatic methods are used, but these are energy-intensive and don’t work when the water is highly saline, as is often the case. Instead, the team explored the use of “photoresponsive” surfaces, whose responses to water can be altered by exposure to light.
By creating surfaces whose interactions with water — a property known as wettability — could be activated by light, the researchers found they could directly separate the oil from the water by causing individual droplets of water to coalesce and spread across the surface. The more the water droplets fuse together, the more they separate from the oil.
Photoresponsive materials have been widely studied and used; one example is the active ingredient in most sunscreens, titanium dioxide, also known as titania. But most of these materials, including titania, respond primarily to ultraviolet light and hardly at all to visible light. Yet only about 5 percent of sunlight is in the ultraviolet range. So the researchers figured out a way to treat the titania surface to make it responsive to visible light.
They did so by first using a layer-by-layer deposition technique to build up a film of polymer-bound titania particles on a layer of glass. Then they dip-coated the material with a simple organic dye. The resulting surface turned out to be highly responsive to visible light, producing a change in wettability when exposed to sunlight that is much greater than that of the titania itself. When activated by sunlight, the material proved very effective at “demulsifying” the oil-water mixture — getting the water and oil to separate from each other.
“We were inspired by the work in photovoltaics, where dye sensitization was used to improve the efficiency of absorption of solar radiation,” says Varansi. “The coupling of the dye to titania particles allows for the generation of charge carriers upon light illumination. This creates an electric potential difference to be established between the surface and the liquid upon illumination, and leads to a change in the wetting properties.”
“Saline water spreads out on our surface under illumination, but oil doesn’t,” says Kwon, who is now an assistant professor at the University of Kansas. “We found that virtually all the seawater will spread out on the surface and get separated from crude oil, under visible light.”
The same effect could also be used to drive droplets of water across a surface, as the team demonstrated in a series of experiments. By selectively changing the material’s wettability using a moving beam of light, a droplet can be directed toward the more wettable area, propelling it in any desired direction with great precision. Such systems could be designed to make microfluidic devices without built-in boundaries or structures. The movement of liquid — for example a blood sample in a diagnostic lab-on-a-chip — would be entirely controlled by the pattern of illumination being projected onto it.
“By systematically studying the relationship between the energy levels of the dye and the wettability of the contacting liquid, we have come up with a framework for the design of these light-guided liquid manipulation systems,” Varanasi says. “By choosing the right kind of dye, we can create a significant change in droplet dynamics. It’s light-induced motion – a touchless motion of droplets.”
The switchable wettability of these surfaces has another benefit: They can be largely self-cleaning. When the surface is switched from water-attracting (hydrophilic) to water-repelling (hydrophobic), any water on the surface gets driven off, carrying with it any contaminants that may have built up.
Since the photoresponsive effect is based on the dye coating, it can be highly tuned by selecting from among the thousands of available organic dyes. All of the materials involved in the process are widely available, inexpensive, commodity materials, the researchers say, and the processes for making them are commonplace.
The research was supported by the King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals, through the Center for Clean Water and Clean Energy at MIT and KFUPM.
###
Written by David L. Chandler, MIT News Office
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Abby Abazorius
MIT News Office
617.253.2709
Copyright © Massachusetts Institute of Technology
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() PAPER: Visible light guided manipulation of liquid wettability on photoresponsive surfaces
PAPER: Visible light guided manipulation of liquid wettability on photoresponsive surfaces
| Related News Press |
Microfluidics/Nanofluidics
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Mining/Extraction/Drilling
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Water
![]() Taking salt out of the water equation October 7th, 2022
Taking salt out of the water equation October 7th, 2022
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








