Home > Press > Pushing a single-molecule switch: An international team of researchers from Donostia International Physics Center, Fritz-Haber Institute of the Max Planck Society, University of Liverpool, and the Polish Academy of Sciences has shown a new way to operate a single-molecule switch
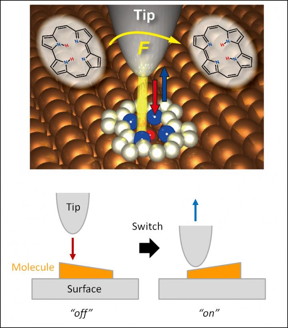 |
| This image represents a single-molecule switch. CREDIT: DIPC |
Abstract:
Everybody knows the force that is required to activate a light switch on a wall - a finger is enough. But how much force do you need to apply if the device was dramatically reduced to the "nanoscale world", that is, how much force do you need to operate a "single-molecule switch"? This fundamental question is related not only to basic science but also to potential future applications of molecular devices.
Pushing a single-molecule switch: An international team of researchers from Donostia International Physics Center, Fritz-Haber Institute of the Max Planck Society, University of Liverpool, and the Polish Academy of Sciences has shown a new way to operate a single-molecule switch
Leioa, Bizkaia | Posted on July 19th, 2016Researchers at Donostia International Physics Center, San Sebastian (Basque Country, Spain), Fritz-Haber Institute of the Max Planck Society, Berlin (Germany), University of Liverpool, (UK) and Polish Academy of Sciences, Warsaw (Poland) have succeeded in activating in a controlled manner a "single-molecule switch" by the force from the atomically-sharp needle of a state-of-the-art scanning probe microscope.
The experimental and theoretical study, reported today in the prestigious journal Nature Chemistry, demonstrates that an intramolecular hydrogen atom transfer can be triggered in a suitable organic molecule adsorbed on a surface by bringing the sharp metallic tip sufficiently close. The reaction, called tautomerization, is important in organic chemistry and molecular biology and also an interesting phenomenon for molecular electronic devices.
The researchers could not only quantify the force needed to operate their tiny switch, a porphycene molecule on a copper surface, but also reveal that the switching can be only induced at a very specific positions of the tip over the molecule, with a spatial resolution of a fraction of a chemical bond length, namely about 0.00000002 millimeter. Furthermore, they demonstrated the significance of the "chemical reactivity" of the tip apex in the force-induced process as the molecule cannot be switched when the apex of the needle is decorated by a single xenon atom - an inert element that lacks the required chemical reactivity.
Takashi Kumagai at FHI-MPG, who conceived this study, constructed the experimental setup in which an oscillating needle of a combined atomic force and scanning tunneling microscope is approached within a few atomic distances to the molecule. The switching showed up as a characteristic feature in the frequency shifts upon approach of the tip and was also confirmed by changes at the atomic-scale images by simultaneously scanning the tip over the molecule. It was measured that the force required was about one nano-Newton, which is a little less than the force needed to break a typical covalent bond between two atoms.
The research team also carried out extensive computer simulations in order to elucidate the atomistic mechanism behind the force-induced switching. The simulations successfully reproduced the experimental results and provided atomistic description on the operation of the single molecule switch. Thomas Frederiksen, Ikerbasque Research Professor at Donostia International Physics Center (DIPC) - UPV/EHU explains that "our calculations revealed that the tautomerization, that is the switching, occurs by a reduction of its energy activation barrier upon approach of a metallic tip. However, the behaviour dramatically changes with a xenon-terminated tip and no tautomerization could be induced because of its inertness and softness".
The researchers emphasize that the studied force-induced reaction involving changes in the reaction pathway resembles an elementary step in catalytic processes. Therefore, their results also provide a novel strategy to gain a deeper atomistic insight into catalytic reactions, leading to a new control of chemistry at the atomic level.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Matxalen Sotillo
34-688-673-770
Copyright © University of Basque Country
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Chemistry
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Molecular Machines
![]() First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
![]() Nanotech scientists create world's smallest origami bird March 17th, 2021
Nanotech scientists create world's smallest origami bird March 17th, 2021
![]() Giant nanomachine aids the immune system: Theoretical chemistry August 28th, 2020
Giant nanomachine aids the immune system: Theoretical chemistry August 28th, 2020
Molecular Nanotechnology
![]() Quantum pumping in molecular junctions August 16th, 2024
Quantum pumping in molecular junctions August 16th, 2024
![]() Scientists push the boundaries of manipulating light at the submicroscopic level March 3rd, 2023
Scientists push the boundaries of manipulating light at the submicroscopic level March 3rd, 2023
![]() First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








