Home > Press > Spintronics: Resetting the future of heat assisted magnetic recording
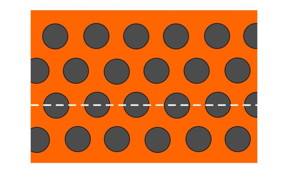 |
| The nanostructured membrane has a honeycomb pattern with nanoholes of 68 nm in diameter. The nanoholes pin down the magnetic domains. CREDIT: HZB |
Abstract:
This paves the way to fast and energy efficient ultrahigh density data storage. The results are published now in the new journal Physical Review Applied.
Spintronics: Resetting the future of heat assisted magnetic recording
Berlin, Germany | Posted on June 15th, 2016To increase data density further in storage media, materials systems with stable magnetic domains on the nanoscale are needed. For overwriting a specific nanoscopic region with new information, a laser is used to heat locally the bit close to the so called Curie-Temperature, typically several hundred degrees Celsius. Upon cooling, the magnetic domain in this region can be reoriented in a small external magnetic field, known as Heat Assisted Magnetic Recording (HAMR). In industry, Iron-Platinum materials are currently used as magnetic media for the development of such HAMR-data storage devices.
Magnetic signals mapped at BESSY II before and after heating
A HZB team has now examined a new storage media system of Dysprosium and Cobalt, which shows key advantages with respect to conventional HAMR materials: A much lower writing temperature, a higher stability of the magnetic bits, and a versatile control of the spin orientation within individual magnetic bits. They achieved this by sputtering a thin film of Dysprosium and Cobalt onto a nanostructured membrane. The membrane was produced by scientific cooperation partners at the Institute of Materials Science of Madrid. The system shows a honeycomb antidot pattern with distances of 105 nanometers between nanoholes, which are 68 nanometers in diameter. These nanoholes act themselves as pinning centers for stabilizing magnetic wall displacements. The magnetic moments of DyCo5 are perpendicular to the plane and stable against external magnetic fields.
Energy efficient process
HZB-physicist Dr. Jaime Sánchez-Barriga and his team could demonstrate that warming the system to only 80 degrees Celsius is sufficient to tilt the magnetic moments in the DyCo5 film parallel to the surface plane. With measurements at the PEEM and XMCD instruments at BESSY II they could map precisely the magnetic signals before, during and after warming. After cooling to room temperature it is then easy to reorient the magnetic domains with a writing head and to encode new information. "This process in DyCo5 is energy efficient and very fast", states Dr. Florin Radu, co-author of the study. "Our results show that there are alternative candidates for ultrahigh density HAMR storage systems, which need less energy and promise other important advantages as well", adds Sánchez-Barriga.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Jaime Sánchez-Barriga
49-308-062-15695
Copyright © Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin für Materialien und Energie (HZB)
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Magnetism/Magnons
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Spintronics
![]() Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Quantum Computing
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Quantum nanoscience
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








