Home > Press > Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time
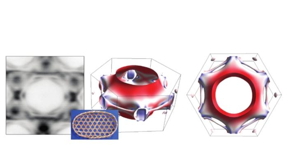 |
| Three perspectives of the surface on which the electrons move. On the left, the experimental result, in the center and on the right the theoretical modeling. The red and blue colors represent a measure of the speed of the electrons. Both theory and experiment reflect the symmetry of the crystal, very similar to the texture of traditional Japanese "kagome" baskets CREDIT University of Bologna |
Abstract:
An international research team has succeeded for the first time in measuring the electron spin in matter - i.e., the curvature of space in which electrons live and move - within "kagome materials", a new class of quantum materials.
Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time
Bologna, Italy | Posted on June 9th, 2023The results obtained - published in Nature Physics - could revolutionise the way quantum materials are studied in the future, opening the door to new developments in quantum technologies, with possible applications in a variety of technological fields, from renewable energy to biomedicine, from electronics to quantum computers.
Success was achieved by an international collaboration of scientists, in which Domenico Di Sante, professor at the Department of Physics and Astronomy "Augusto Righi", participated for the University of Bologna as part of his Marie Curie BITMAP research project. He was joined by colleagues from CNR-IOM Trieste, Ca' Foscari University of Venice, University of Milan, University of Würzburg (Germany), University of St. Andrews (UK), Boston College and University of Santa Barbara (USA).
Through advanced experimental techniques, using light generated by a particle accelerator, the Synchrotron, and thanks to modern techniques for modelling the behaviour of matter, the scholars were able to measure electron spin for the first time, related to the concept of topology.
"If we take two objects such as a football and a doughnut, we notice that their specific shapes determine different topological properties, for example because the doughnut has a hole, while the football does not," Domenico Di Sante explains. "Similarly, the behaviour of electrons in materials is influenced by certain quantum properties that determine their spinning in the matter in which they are found, similar to how the trajectory of light in the universe is modified by the presence of stars, black holes, dark matter, and dark energy, which bend time and space."
Although this characteristic of electrons has been known for many years, no one had until now been able to measure this "topological spin" directly. To achieve this, the researchers exploited a particular effect known as "circular dichroism": a special experimental technique that can only be used with a synchrotron source, which exploits the ability of materials to absorb light differently depending on their polarisation.
Scholars have especially focused on "kagome materials", a class of quantum materials that owe their name to their resemblance to the weave of interwoven bamboo threads that make up a traditional Japanese basket (called, indeed, "kagome"). These materials are revolutionising quantum physics, and the results obtained could help us learn more about their special magnetic, topological, and superconducting properties.
"These important results were possible thanks to a strong synergy between experimental practice and theoretical analysis," adds Di Sante. "The team's theoretical researchers employed sophisticated quantum simulations, only possible with the use of powerful supercomputers, and in this way guided their experimental colleagues to the specific area of the material where the circular dichroism effect could be measured.
The study was published in Nature Physics with the title "Flat band separation and robust spin Berry curvature in bilayer kagome metals". The first author of the study is Domenico Di Sante, a researcher at the "Augusto Righi" Department of Physics and Astronomy of the University of Bologna. He worked with scholars from the CNR-IOM of Trieste, the Ca' Foscari University of Venice, the University of Milan, the University of Würzburg (Germany), the University of St. Andrews (UK), the Boston College and the University of Santa Barbara (USA).
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Matteo Benni
Università di Bologna
Office: 39-338-786-6108
Copyright © Università di Bologna
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Quantum Physics
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Quantum chemistry
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Three-pronged approach discerns qualities of quantum spin liquids November 17th, 2023
Three-pronged approach discerns qualities of quantum spin liquids November 17th, 2023
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Spintronics
Quantum Computing
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Quantum nanoscience
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








