Home > Press > Innovative catalyst fabrication method may yield breakthrough in fuel cell development: Kyushu University research group develops new method for creating highly efficient gold nanoparticle catalysts for fuel cells
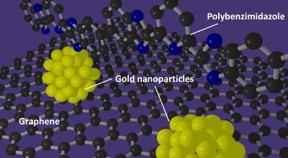 |
| A polybenzimidazole polymer supports the formation of gold nanoparticles with well-defined sizes on graphene. CREDIT: International Institute for Carbon-Neutral Energy Research (I˛CNER), Kyushu University |
Abstract:
The successful future of fuel cells relies on improving the performance of the catalysts they use. Gold nanoparticles have been cited as an ideal solution, but creating a uniform, useful catalyst has proven elusive. However, a team of researchers at Kyushu University's International Institute for Carbon-Neutral Energy Research (I2CNER) devised a method for using a new type of catalyst support.
Innovative catalyst fabrication method may yield breakthrough in fuel cell development: Kyushu University research group develops new method for creating highly efficient gold nanoparticle catalysts for fuel cells
Fukuoka, Japan | Posted on March 9th, 2016In a potential breakthrough technology for fuel cells, a recently published article in Scientific Reports shows how wrapping a graphene support in a specially prepared polymer provides an ideal foundation for making uniform, highly active gold nanoparticle catalysts.
Fuel cells produce electricity directly from the separate oxidation of the fuel and the reduction of oxygen. The only by-product of the process is water, as fuel cells produce no greenhouse gases and are widely seen as essential for a clean-energy future.
However, the rate at which electricity can be produced in fuel cells is limited, especially by the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR), which must be catalyzed in practical applications. Although current platinum-based catalysts accelerate the reaction, their unhelpful propensity to also catalyze other reactions, and their sensitivity to poisoning by the reactants, limits their overall utility. Despite bulk gold being chemically inert, gold nanoparticles are surprisingly effective at catalyzing the oxygen reduction reaction without the drawbacks associated with their platinum counterparts.
Nevertheless, actually creating uniformly sized gold nanoparticle catalysts has proven problematic. Previous fabrication methods have produced catalysts with nanoparticle sizes that were too large or too widely distributed for practical use. Meanwhile, efforts to regulate the particle size tended to restrict the gold's activity or make less-stable catalysts.
"Creating small, well-controlled particles meant that we needed to focus on particle nucleation and particle growth," lead and corresponding author Tsuyohiko Fujigaya says. "By wrapping the support in the polybenzimidazole polymer we successfully developed with platinum, we created a much better support environment for the gold nanoparticles."
The team also tested the performance of these novel catalyst structures. Their catalysts had the lowest overpotential ever reported for this type of reaction. "The overpotential is a bit like the size of the spark you need to start a fire," coauthor Naotoshi Nakashima says. "Although we're obviously pleased with the catalysts' uniformity, the performance results show this really could be a leap forward for the ORR reaction and maybe fuel cells as well."
Although novel in its own right, this recent publication is the latest in a chain of developments that the interdisciplinary teams at I2CNER have been carrying out to develop fuel cells and other clean technologies.
####
About Kyushu University, I2CNER
I2CNER's mission is to contribute to the advancement of low carbon emission and cost effective energy systems and improvement of energy efficiency. The array of technologies that I2CNER's research aims to enable includes Solid Oxide Fuel Cells, Polymer Membrane based fuel cells, biomimetic and other novel catalyst concepts, and production, storage, and utilization of hydrogen as a fuel. Our research also explores the underlying science of CO2 capture and storage or the conversion of CO2 to a useful product. Additionally, central to I2CNER's mission is the establishment of an international academic environment that fosters innovation through collaboration and interdisciplinary research.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Yumiko Masumoto
81-928-026-935
Research Contact:
Naotoshi Nakashima
International Institute for Carbon-Neutral Energy Research (I˛CNER)
Kyushu University
nakashima-tcm_at_mail.cstm.kyushu-u.ac.jp
Copyright © Kyushu University, I2CNER
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Chemistry
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Single-atom catalysts change spin state when boosted by a magnetic field June 4th, 2025
Single-atom catalysts change spin state when boosted by a magnetic field June 4th, 2025
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Automotive/Transportation
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Fuel Cells
![]() Deciphering local microstrain-induced optimization of asymmetric Fe single atomic sites for efficient oxygen reduction August 8th, 2025
Deciphering local microstrain-induced optimization of asymmetric Fe single atomic sites for efficient oxygen reduction August 8th, 2025
![]() Current and Future Developments in Nanomaterials and Carbon Nanotubes: Applications of Nanomaterials in Energy Storage and Electronics October 28th, 2022
Current and Future Developments in Nanomaterials and Carbon Nanotubes: Applications of Nanomaterials in Energy Storage and Electronics October 28th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








