Home > Press > Flexible battery, no lithium required: Rice University lab creates thin-film battery for portable, wearable electronics
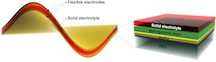 |
| Nickel-fluoride electrodes around a solid electrolyte are an effective energy storage device that combines the best qualities of batteries and supercapacitors, according to Rice University researchers. The electrodes are plated onto a gold and polymer backing (which can be removed) and made porous through a chemical etching process. Credit: Tour Group/Rice University |
Abstract:
A Rice University laboratory has flexible, portable and wearable electronics in its sights with the creation of a thin film for energy storage.
Flexible battery, no lithium required: Rice University lab creates thin-film battery for portable, wearable electronics
Houston, TX | Posted on April 28th, 2014Rice chemist James Tour and his colleagues have developed a flexible material with nanoporous nickel-fluoride electrodes layered around a solid electrolyte to deliver battery-like supercapacitor performance that combines the best qualities of a high-energy battery and a high-powered supercapacitor without the lithium found in commercial batteries today.
The new work by the Rice lab of chemist James Tour is detailed in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
Their electrochemical capacitor is about a hundredth of an inch thick but can be scaled up for devices either by increasing the size or adding layers, said Rice postdoctoral researcher Yang Yang, co-lead author of the paper with graduate student Gedeng Ruan. They expect that standard manufacturing techniques may allow the battery to be even thinner.
In tests, the students found their square-inch device held 76 percent of its capacity over 10,000 charge-discharge cycles and 1,000 bending cycles.
Tour said the team set out to find a material that has the flexible qualities of graphene, carbon nanotubes and conducting polymers while possessing much higher electrical storage capacity typically found in inorganic metal compounds. Inorganic compounds have, until recently, lacked flexibility, he said.
"This is not easy to do, because materials with such high capacity are usually brittle," he said. "And we've had really good, flexible carbon storage systems in the past, but carbon as a material has never hit the theoretical value that can be found in inorganic systems, and nickel fluoride in particular."
"Compared with a lithium-ion device, the structure is quite simple and safe," Yang said. "It behaves like a battery but the structure is that of a supercapacitor. If we use it as a supercapacitor, we can charge quickly at a high current rate and discharge it in a very short time. But for other applications, we find we can set it up to charge more slowly and to discharge slowly like a battery."
To create the battery/supercapacitor, the team deposited a nickel layer on a backing. They etched it to create 5-nanometer pores within the 900-nanometer-thick nickel fluoride layer, giving it high surface area for storage. Once they removed the backing, they sandwiched the electrodes around an electrolyte of potassium hydroxide in polyvinyl alcohol. Testing found no degradation of the pore structure even after 10,000 charge/recharge cycles. The researchers also found no significant degradation to the electrode-electrolyte interface.
"The numbers are exceedingly high in the power that it can deliver, and it's a very simple method to make high-powered systems," Tour said, adding that the technique shows promise for the manufacture of other 3-D nanoporous materials. "We're already talking with companies interested in commercializing this."
Rice graduate student Changsheng Xiang and postdoctoral researcher Gunuk Wang are co-authors of the paper.
The Peter M. and Ruth L. Nicholas Postdoctoral Fellowship of the Smalley Institute for Nanoscale Science and Technology and the Air Force Office of Scientific Research's Multidisciplinary University Research Initiative supported the research.
####
About Rice University
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation’s top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is home to the Baker Institute for Public Policy. With 3,920 undergraduates and 2,567 graduate students, Rice’s undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is 6.3-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice has been ranked No. 1 for best quality of life multiple times by the Princeton Review and No. 2 for “best value” among private universities by Kiplinger’s Personal Finance.
Follow Rice News and Media Relations via Twitter @RiceUNews
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
David Ruth
713-348-6327
Mike Williams
713-348-6728
Copyright © Rice University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Richard E. Smalley Institute for Nanoscale Science and Technology:
Richard E. Smalley Institute for Nanoscale Science and Technology:
| Related News Press |
Thin films
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Flexible Electronics
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() Flexible electronics integrated with paper-thin structure for use in space January 17th, 2025
Flexible electronics integrated with paper-thin structure for use in space January 17th, 2025
![]() Beyond wires: Bubble technology powers next-generation electronics:New laser-based bubble printing technique creates ultra-flexible liquid metal circuits November 8th, 2024
Beyond wires: Bubble technology powers next-generation electronics:New laser-based bubble printing technique creates ultra-flexible liquid metal circuits November 8th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








