Home > Press > Gold nanoparticles create visible-light catalysis in nanowires
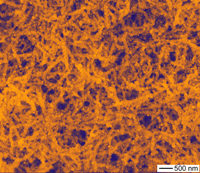 |
| The gold-coated silver chloride nanowires at the microscopic level |
Abstract:
A scientist at the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory has created visible-light catalysis, using silver chloride nanowires decorated with gold nanoparticles, that may decompose organic molecules in polluted water.
Gold nanoparticles create visible-light catalysis in nanowires
Argonne, IL | Posted on June 16th, 2010"Silver nanowires have been extensively studied and used for a variety of applications, including transparent conductive electrodes for solar cells and optoelectronic devices," said nanoscientist Yugang Sun of Argonne's Center for Nanoscale Materials. "By chemically converting them into semiconducting silver chloride nanowires, followed by adding gold nanoparticles, we have created nanowires with a completely new set of properties that are significantly different from the original nanowires."
Traditional silver chloride photocatalytic properties are restricted to ultraviolet and blue light wavelengths, but with the addition of the gold nanoparticles, they become photocatalytic in visible light. The visible light excites the electrons in the gold nanoparticles and initiates reactions that culminate in charge separation on the silver chloride nanowires. Tests have already shown that gold-decorated nanowires can decompose organic molecules such as methylene blue.
"If you were to create a film of gold-decorated nanowires and allow polluted water to flow through it, the organic molecules may be destroyed with visible irradiation from conventional fluorescent light bulbs or the sun," Sun said.
Sun started with traditional silver nanowires that were oxidized with iron chloride to create silver chloride nanowires. A sequential reaction with sodium tetrachloroaurate deposited the gold nanoparticles on the wires.
Sun said it is possible to use a similar mechanism to deposit other metals such as palladium and platinum onto the silver chloride nanowires and create new properties, such as the ability to catalyze the splitting of water into hydrogen with sunlight.
A paper on this research was published in the Journal of Physical Chemistry C pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jp9115645
Funding was provided by the U.S. Department of Energy Office of Science.
The Center for Nanoscale Materialsat Argonne National Laboratory is one of the five DOE Nanoscale Science Research Centers (NSRCs), premier national user facilities for interdisciplinary research at the nanoscale, supported by the DOE Office of Science. Together the NSRCs comprise a suite of complementary facilities that provide researchers with state-of-the-art capabilities to fabricate, process, characterize and model nanoscale materials, and constitute the largest infrastructure investment of the National Nanotechnology Initiative. The NSRCs are located at DOE's Argonne, Brookhaven, Lawrence Berkeley, Oak Ridge and Sandia and Los Alamos national laboratories.
More information about the DOE NSRCs is available online at www.science.doe.gov/news_information/news_room/2006/nano/index.htm
####
About Argonne National Laboratory
Argonne National Laboratory seeks solutions to pressing national problems in science and technology. The nation's first national laboratory, Argonne conducts leading-edge basic and applied scientific research in virtually every scientific discipline. Argonne researchers work closely with researchers from hundreds of companies, universities, and federal, state and municipal agencies to help them solve their specific problems, advance America 's scientific leadership and prepare the nation for a better future. With employees from more than 60 nations, Argonne is managed by UChicago Argonne, LLC for the U.S. Department of Energy's Office of Science.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Brock Cooper
630/252-5565
Copyright © Argonne National Laboratory
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Chemistry
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Environment
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Water
![]() Taking salt out of the water equation October 7th, 2022
Taking salt out of the water equation October 7th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








