Home > Press > Getting to the root of tooth replantation challenges: Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) report a delivery system that promotes healing in tooth replantation in rats
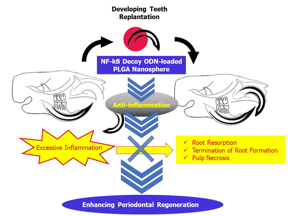 |
| Excessive inflammation after tooth replantation induces several omplications including root resorption, termination of root formation and pulp necrosis, caused by excessive inflammation. NF-kB decoy ODN-loaded PLGA nanosphere inhibits post-operative inflammation, thus enhances periodontal regeneration, including reduction of root resorption, and continuation of root formation. CREDIT Department of Orthodontic Science, TMDU |
Abstract:
Completely dislodging a tooth from the socket is not generally considered a reversible process. However, this injury is most common in children, whose roots may not be completely developed, meaning quick reactions could save the tooth. Researchers are continually looking to increase the chance of success in tooth replantation. Now, a team led by researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) has reported a gene delivery system that promotes the healing process in a rat model. Their findings are published in Journal of Periodontology.
Getting to the root of tooth replantation challenges: Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) report a delivery system that promotes healing in tooth replantation in rats
Tokyo, Japan | Posted on September 17th, 2021Replanting a tooth as quickly as possible after it is knocked out provides its best chance of survival. Speed ensures that the periodontal ligament (PDL)—the tissue that holds the tooth in place—and dental pulp do not start to die. Fibers can then reattach, and the blood vessels and pulp tissue can continue to grow and support the tooth.
However, many factors can affect the success of replantation—for example, inflammation—which can stop the PDL regenerating.
One of the messaging pathways that controls inflammation is the nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) pathway. Activation of this pathway produces the proteins that induce inflammation. And inflammation leads to osteoclasts—bone degrading cells—breaking down the tissue around the root of the tooth, often spelling the end of any hope of successful replantation.
A recently reported way of stopping the NF-κB pathway is to use NF-κB decoy oligodeoxynucleotides (ODNs), which prevent NF-κB biding to its target genes. However, getting the large NF-κB decoy ODNs to where they need to be to have an effect can be challenging.
The TMDU researchers loaded NF-κB decoy ODNs into poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanospheres to give NF-PGLA. Incorporating the therapeutic cargo into the nanosphere system protected it until it reached the site of action.
“We tested our delivery system in rats by immersing extracted incisors in different solutions before replanting them,” explains study first author Kai Li. “We found that the teeth treated with NF-PGLA showed significantly greater dental root thickness, which is necessary for successful replantation.”
The researchers also found that no root resorption—dissolving of the tooth root—was observed 7 days after treatment with NF-PGLA. In addition, there were fewer osteoclasts 7 and 14 days after replantation for NF-PGLA-treated teeth.
“Application of our NF-PGLA system encouraged the healing process by preventing the exacerbation of inflammation,” says study corresponding author Yuji Ishida. “We believe that our delivery system will contribute to significantly improving the success of tooth replantation in the clinic,” adds principal investigator Takashi Ono.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Takashi Ono
Tokyo Medical and Dental University
Expert Contact
Yuji Ishida
Tokyo Medical and Dental University
Copyright © Tokyo Medical and Dental University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Dental
![]() Innovations in dentistry: Navigational surgery, robotics, and nanotechnology October 2nd, 2020
Innovations in dentistry: Navigational surgery, robotics, and nanotechnology October 2nd, 2020
![]() First measurement of electron energy distributions, could enable sustainable energy technologies June 5th, 2020
First measurement of electron energy distributions, could enable sustainable energy technologies June 5th, 2020
![]() Gas storage method could help next-generation clean energy vehicles: Tremendous amounts of hydrogen and methane can be stored in nanoscopic pores April 17th, 2020
Gas storage method could help next-generation clean energy vehicles: Tremendous amounts of hydrogen and methane can be stored in nanoscopic pores April 17th, 2020
![]() Novel nanoparticle-based approach detects and treats oral plaque without drugs August 17th, 2018
Novel nanoparticle-based approach detects and treats oral plaque without drugs August 17th, 2018
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








