Home > Press > Novel nanoparticle-based approach detects and treats oral plaque without drugs
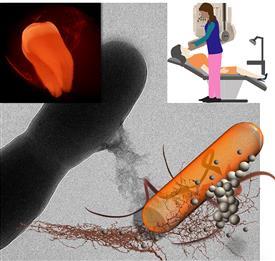 |
| In this illustration, nanoparticles attach to or are taken up by the bacteria cells. Pan and his students are the first group to demonstrate that early detection of dental plaque in the clinic is possible using the regular intraoral X-ray machine which can seek out harmful bacteria populations. CREDIT University of Illinois Laboratory for Materials in Medicine. In this illustration, nanoparticles attach to or are taken up by the bacteria cells. Pan and his students are the first group to demonstrate that early detection of dental plaque in the clinic is possible using the regular intraoral X-ray machine which can seek out harmful bacteria populations. CREDIT University of Illinois Laboratory for Materials in Medicine. |
Abstract:
When the good and bad bacteria in our mouth become imbalanced, the bad bacteria form a biofilm (aka plaque), which can cause cavities, and if left untreated over time, can lead to cardiovascular and other inflammatory diseases like diabetes and bacterial pneumonia.
Novel nanoparticle-based approach detects and treats oral plaque without drugs
Urbana, IL | Posted on August 17th, 2018A team of researchers from the University of Illinois has recently devised a practical nanotechnology-based method for detecting and treating the harmful bacteria that cause plaque and lead to tooth decay and other detrimental conditions.
Bioengineering Associate Professor Dipanjan Pan (seated) and doctoral student Fatemeh Ostadhossein have demonstrated a drug-free, nanotechnology-based method for detecting and destroying the bacteria that causes dental plaque.
Oral plaque is invisible to the eye so dentists currently visualize it with disclosing agents, which they administer to patients in the form of a dissolvable tablet or brush-on swab. While useful in helping patients see the extent of their plaque, these methods are unable to identify the difference between good and bad bacteria.
"Presently in the clinic, detection of dental plaque is highly subjective and only depends on the dentist's visual evaluation," said Bioengineering Associate Professor Dipanjan Pan, head of the research team. "We have demonstrated for the first time that early detection of dental plaque in the clinic is possible using the regular intraoral X-ray machine which can seek out harmful bacteria populations."
In order to accomplish this, Fatemeh Ostadhossein, a Bioengineering graduate student in Pan's group, developed a plaque detection probe that works in conjunction with common X-ray technology and which is capable of finding specific harmful bacteria known as Streptococcus mutans (S. mutans) in a complex biofilm network. Additionally, they also demonstrated that by tweaking the chemical composition of the probe, it can be used to target and destroy the S. mutans bacteria.
The probe is comprised of nanoparticles made of hafnium oxide (HfO2), a non-toxic metal that is currently under clinical trial for internal use in humans. In their study, the team demonstrated the efficacy of the probe to identify biochemical markers present at the surface of the bacterial biofilm and simultaneously destroy S. mutans. They conducted their study on Sprague Dawley rats.
In practice, Pan envisions a dentist applying the probe on the patient's teeth and using the X-ray machine to accurately visualize the extent of the biofilm plaque. If the plaque is deemed severe, then the dentist would follow up with the administering of the therapeutic HfO2 nanoparticles in the form of a dental paste.
In their study, the team compared the therapeutic ability of their nanoparticles with Chlorhexidine, a chemical currently used by dentists to eradicate biofilm. "Our HfO2 nanoparticles are far more efficient at killing the bacteria and reducing the biofilm burden both in cell cultures of bacteria and in [infected] rats," said Ostadhossein, noting that their new technology is also much safer than conventional treatment.
The nanoparticles' therapeutic effect is due, said Pan, to their unique surface chemistry, which provides a latch and kill mechanism. "This mechanism sets our work apart from previously pursued nanoparticle-based approaches where the medicinal effect comes from anti-biotics encapsulated in the particles," said Pan, also a faculty member of the Carle Illinois College of Medicine and the Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology. "This is good because our approach avoids anti-biotic resistance issues and it's safe and highly scalable, making it well-suited for eventual clinical translation."
In addition to Pan and Ostadhossein, other members of the research team include bioengineering post-doctoral researcher Santosh Misra, visiting scholar Indu Tripathi, undergraduate Valeriya Kravchuk, visiting scholar Gururaja Vulugundam; and Veterinary Medicine clinical assistant professor Denae LoBato and adjunct assistant professor Laura Selmic.
###
Their work is described in the paper, "Dual purpose hafnium oxide nanoparticles offer imaging Streptococcus mutans dental biofilm and fight it In vivo via a drug free approach," published online on July 30, 2018, in the journal Biomaterials. The research was funded by the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Children's Discovery Institute and the American Heart Association.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Dipanjan Pan
217-244-2938
Copyright © University of Illinois College of Engineering
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Dental
![]() Innovations in dentistry: Navigational surgery, robotics, and nanotechnology October 2nd, 2020
Innovations in dentistry: Navigational surgery, robotics, and nanotechnology October 2nd, 2020
![]() First measurement of electron energy distributions, could enable sustainable energy technologies June 5th, 2020
First measurement of electron energy distributions, could enable sustainable energy technologies June 5th, 2020
![]() Gas storage method could help next-generation clean energy vehicles: Tremendous amounts of hydrogen and methane can be stored in nanoscopic pores April 17th, 2020
Gas storage method could help next-generation clean energy vehicles: Tremendous amounts of hydrogen and methane can be stored in nanoscopic pores April 17th, 2020
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








