Home > Press > Researchers reduce expensive noble metals for fuel cell reactions
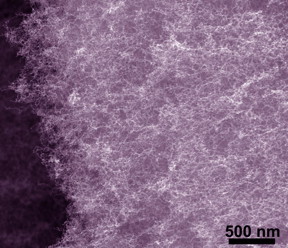 |
| Bi-metallic aerogels at the nanoscale have good porosity and a large surface area, which work well for catalytic reactions in fuel cells. CREDIT: Washington State University |
Abstract:
Washington State University researchers have developed a novel nanomaterial that could improve the performance and lower the costs of fuel cells by using fewer precious metals like platinum or palladium.
Researchers reduce expensive noble metals for fuel cell reactions
Pullman, WA | Posted on August 22nd, 2016Led by Yuehe Lin, professor in the School of Mechanical and Materials Engineering, the researchers used inexpensive metal to make a super low density material, called an aerogel, to reduce the amount of precious metals required for fuel cell reactions. They also sped up the time to make the aerogels, which makes them more viable for large-scale production.
Their work is published in Advanced Materials.
Hydrogen fuel cells are a promising green energy solution, producing electricity much more efficiently and cleanly than combustion engines. But they need expensive precious metals to fuel their chemical reactions. This need has limited their acceptance in the marketplace.
Aerogels, which are sometimes also called liquid smoke, are solid materials that are about 92 percent air. Effective insulators, they are used in wet suits, firefighting gear, windows, paints and in fuel cell catalysts. Because metal-based aerogels have large surface areas and are highly porous, they work well for catalyzing in fuel cells.
The WSU team created a series of bimetallic aerogels, incorporating inexpensive copper and using less precious metal than other metal aerogels.
Researchers introduced the copper in the bimetallic system through their new, one-step reduction method to create hydrogel. The hydrogel is the liquid-filled form of aerogel. The liquid component is carefully and completely dried out of the hydrogel to create aerogel. Their method has reduced the manufacturing time of hydrogel from three days to six hours.
"This will be a great advantage for large scale production," said Chengzhou Zhu, a WSU assistant research professor who created the aerogel.
The research is in keeping with WSU's Grand Challenges, a suite of research initiatives aimed at large societal issues. It is particularly relevant to the challenge of sustainable resources and its theme of energy.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Yuehe Lin
509-335-8523
Copyright © Washington State University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Hydrogels
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
![]() Shrinking hydrogels enlarge nanofabrication options: Researchers from Pittsburgh and Hong Kong print intricate, 2D and 3D patterns December 29th, 2022
Shrinking hydrogels enlarge nanofabrication options: Researchers from Pittsburgh and Hong Kong print intricate, 2D and 3D patterns December 29th, 2022
![]() The deformation of the hydrogel is used to measure the negative pressure of water April 22nd, 2022
The deformation of the hydrogel is used to measure the negative pressure of water April 22nd, 2022
![]() Nanocellulose decorated with proteins is suitable for 3D cell culturing September 24th, 2021
Nanocellulose decorated with proteins is suitable for 3D cell culturing September 24th, 2021
Aerogels
![]() The lightest shielding material in the world: Protection against electromagnetic interference July 3rd, 2020
The lightest shielding material in the world: Protection against electromagnetic interference July 3rd, 2020
![]() Super-light, super-insulating ceramic aerogel keeps the hottest temperatures at bay February 17th, 2019
Super-light, super-insulating ceramic aerogel keeps the hottest temperatures at bay February 17th, 2019
![]() Aspen Aerogels to Present at the 28th Annual ROTH Conference March 14th, 2016
Aspen Aerogels to Present at the 28th Annual ROTH Conference March 14th, 2016
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Automotive/Transportation
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Fuel Cells
![]() Deciphering local microstrain-induced optimization of asymmetric Fe single atomic sites for efficient oxygen reduction August 8th, 2025
Deciphering local microstrain-induced optimization of asymmetric Fe single atomic sites for efficient oxygen reduction August 8th, 2025
![]() Current and Future Developments in Nanomaterials and Carbon Nanotubes: Applications of Nanomaterials in Energy Storage and Electronics October 28th, 2022
Current and Future Developments in Nanomaterials and Carbon Nanotubes: Applications of Nanomaterials in Energy Storage and Electronics October 28th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








