Home > Press > Nanocellulose decorated with proteins is suitable for 3D cell culturing
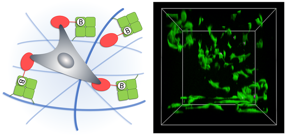 |
| Schematic presentation showing avidin-conjugated nanocellulose fibers functionalized with biotinylated adhesive protein. 3D cell culture of fibroblast cells. Live-dead staining indicates high cell viability. CREDIT Reprinted with permission from Leppiniemi et al. Biomacromolecules. Copyright 2021 American Chemical Society. |
Abstract:
Wood-derived cellulose nanofibers form a hydrogel in water, referred to as nanocellulose, which is a highly promising material for various biological applications. However, nanocellulose is rather simple in terms of chemical composition compared to the natural environment of cells in living tissue. To enable the tailoring of nanocellulose-based hydrogels, researchers from Tampere University in Finland, in collaboration with researchers from UPM Biomedicals, developed avidin-conjugated nanocellulose. Such material enables the attachment of biotinylated molecules on avidin-conjugated nanocellulose fibers.
Nanocellulose decorated with proteins is suitable for 3D cell culturing
Kauppi, Finland | Posted on September 24th, 2021“We utilized a protein named avidin – which is originally isolated from chicken eggs – that binds the biotin vitamin with extremely high affinity. Biotin can be chemically attached to various biomolecules without compromising its activity”, says Postdoctoral Researcher Jenni Leppiniemi, who is the principal investigator in the project working in a group led by Professor Vesa Hytönen.
“The benefit of avidin-conjugated nanocellulose is that it can be tailored and functionalized as necessary by choosing different biotinylated molecules for different applications,” Leppiniemi explains. When the avidin-conjugated nanocellulose fibers were functionalized with biotinylated proteins originating from extracellular matrix, a 3D hydrogel was obtained, which offers plausible attachment sites for cells. The cells were found to proliferate quicker in the functionalized hydrogel compared to bare nanocellulose, and the cell viability remained high during the experiment.
These findings indicate that the developed material was highly suitable for the 3D culturing of cells. The cells also showed signs of being associated with efficient integrin signaling indicating that they have the capacity to attach tightly to functionalized nanocellulose.
Avidin-conjugated nanocellulose offers promising possibilities for applications requiring tailored hydrogels, such as cell differentiation and tissue engineering. Product Development Scientist Piia Mikkonen from UPM Biomedicals suggests that the developed material could be a potential alternative to animal-derived hydrogel materials, which are complicated in their composition and poorly defined chemically.
###
The results of the project were published in the Biomacromolecules journal.
Jenni Leppiniemi, Zeeshan Mutahir, Alexander Dulebo, Piia Mikkonen, Markus Nuopponen, Paula Turkki, and Vesa Hytönen: Avidin-Conjugated Nanofibrillar Cellulose Hydrogel Functionalized with Biotinylated Fibronectin and Vitronectin Promotes 3D Culture of Fibroblasts
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Pirjo Achte
Tampere University
Office: 358-504-336-290
Copyright © Tampere University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Hydrogels
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
![]() Shrinking hydrogels enlarge nanofabrication options: Researchers from Pittsburgh and Hong Kong print intricate, 2D and 3D patterns December 29th, 2022
Shrinking hydrogels enlarge nanofabrication options: Researchers from Pittsburgh and Hong Kong print intricate, 2D and 3D patterns December 29th, 2022
![]() The deformation of the hydrogel is used to measure the negative pressure of water April 22nd, 2022
The deformation of the hydrogel is used to measure the negative pressure of water April 22nd, 2022
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








