Home > Press > DNA dominos on a chip: Carriers of genetic information packed together on a biochip like in nature
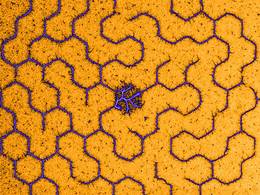 |
| Labyrinth of condensed DNA molecules. Photo: G. Pardatscher / TUM |
Abstract:
Normally, individual molecules of genetic material repel each other. However, when space is limited DNA molecules must be packed together more tightly. This case arises in sperm, cell nuclei and the protein shells of viruses. An international team of physicists has now succeeded in artificially recreating this so-called DNA condensation on a biochip.
DNA dominos on a chip: Carriers of genetic information packed together on a biochip like in nature
Munich, Germany | Posted on August 11th, 2016Recreating important biological processes in cells to better understand them currently is a major topic of research. Now, physicists at TU Munich and the Weizmann Institute in Rehovot have for the first time managed to carry out controlled, so-called DNA condensation on a biochip. This process comes into play whenever DNA molecules are closely packed into tight spaces, for example in circumstances that limit the available volume.
This situation arises in cell nuclei and in the protein shells of viruses, as well as in the heads of sperm cells. The phenomenon is also interesting from a physical perspective because it represents a phase transition, of sorts. DNA double helices, which normally repel each other because of their negative charges, are then packed together tightly. "In this condensed state they take on a nearly crystalline structure," says co-author and TU professor Friedrich Simmel.
Nano hairs
The international team led by Simmel and his Israeli colleague Roy Bar-Ziv managed to bond DNA molecules only one thousandth of a millimeter long (i.e. several thousand base pairs long each) tightly to nanostructures of varying widths on a chip. The result looks as though the researchers had planted tiny hairs onto the chip surface.
Due to their negative charge, DNA molecules repel each other, giving the appearance of tiny nanohairs standing on end. The process of condensation was initiated when the researchers added an agent called spermidine, whose molecules have multiple positive charges. The previously upright DNA threads collapsed one after the other, dropping systematically onto the fine structures of the next thread.
This is like a domino cascade at the nanoscale. The result was compact layers of DNA molecules, packed as densely as they are in cell nuclei. All DNA molecules fell along the predefined path. "This is a very dramatic process," says Simmel. "The DNA is instantly bundled in a single direction."
Condensation and decondensation, i.e. the renewed unpacking of DNA strands, play an important role in processes like gene expression. When the DNA molecules are densely packed, for example, the information coded in them cannot be read.
New insight from the DNA chip
The researchers thus have a further building block for creating artificial cells on the surface of chips and studying all associated phenomena. "It is quite plausible to implement cell-like systems with densely packed DNA on a chip," says Simmel. DNA condensation could then be used to improve the control of gene expression and copying of genetic information in these kinds of artificial cells.
In principle, it is also possible to use the densely packed DNA molecules to relay and distribute signals and information via a kind of conducting path on such biochips. Condensation and decondensation could be used as on/off switches with good temporal control.
Friedrich Simmel would not be a passionate researcher if he did not, in addition to technical application perspectives, have his eye on basic physics. "We also want to understand the conditions of the phase transition during condensation," says Simmel. "For this we have ideal conditions on the chip. We can precisely control where the condensation occurs and how long it takes."
This is somewhat like supercooled water or beer in the freezer box, in which the liquid freezes abruptly starting at a specific point with a crystallization seed and then spreads outwards from there. The only difference is that the phase transition is not controlled by temperature, but rather the concentration of positively charged molecules. The research was funded by the Volkswagen Foundation, the German Research Foundation via the Excellence Cluster Nanosystems Initiative Munich (NIM), the Israel Science Foundation and the Minerva 80 Foundation.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Stefanie Reiffert
49-892-891-0519
Technical University of Munich
Prof. Friedrich C. Simmel
Department of Physics and ZNN/WSI
Tel: +49 89 289 11610
Copyright © Technical University of Munich (TUM)
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Organic Electronics
![]() Unveiling the power of hot carriers in plasmonic nanostructures August 16th, 2024
Unveiling the power of hot carriers in plasmonic nanostructures August 16th, 2024
![]() Efficient and stable hybrid perovskite-organic light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40 per cent July 5th, 2024
Efficient and stable hybrid perovskite-organic light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40 per cent July 5th, 2024
![]() New organic molecule shatters phosphorescence efficiency records and paves way for rare metal-free applications July 5th, 2024
New organic molecule shatters phosphorescence efficiency records and paves way for rare metal-free applications July 5th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Molecular Nanotechnology
![]() Quantum pumping in molecular junctions August 16th, 2024
Quantum pumping in molecular junctions August 16th, 2024
![]() Scientists push the boundaries of manipulating light at the submicroscopic level March 3rd, 2023
Scientists push the boundaries of manipulating light at the submicroscopic level March 3rd, 2023
![]() First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
Chip Technology
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
![]() Physicists unlock the secret of elusive quantum negative entanglement entropy using simple classical hardware August 16th, 2024
Physicists unlock the secret of elusive quantum negative entanglement entropy using simple classical hardware August 16th, 2024
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








