Home > Press > Breaking metamaterial symmetry with reflected light: A group of UK researchers has discovered a new type of optical activity by breaking the symmetry of metamaterials with reflected light
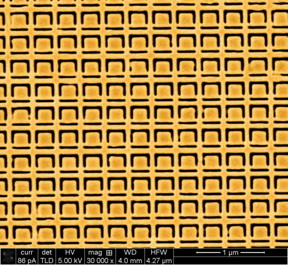 |
| This gold metamaterial nanostructure is a nanoscale version of the structure described by the University of Southampton researchers in Applied Physics Letters, and it exhibits large specular optical activity for oblique incidence illumination with light (rather than specular optical activity for microwaves). CREDIT: Eric Plum, Vassili A. Fedotov, and Nikolay I. Zheludev |
Abstract:
Optical activity--rotation of the polarization of light--is well known to occur within materials that differ from their mirror image. But what happens if this symmetry is broken by the direction of illumination rather than the material itself?
Breaking metamaterial symmetry with reflected light: A group of UK researchers has discovered a new type of optical activity by breaking the symmetry of metamaterials with reflected light
Washington, DC | Posted on April 5th, 2016Curiosity about this question has led to the discovery of a new type of optical activity. As a group of University of Southampton researchers report in Applied Physics Letters, from AIP Publishing, breaking the symmetry of metamaterials with reflected light will enable novel applications because it causes optical activity of unprecedented magnitude--far exceeding previously known specular or "mirror-like" optical activity.
At the heart of the group's work are metamaterials--materials constructed with unique shapes and symmetries that generate properties which don't occur in their natural counterparts.
"Natural materials derive their properties from the atoms, ions, or molecules they consist of. Similarly, the basic concept behind metamaterials is to assemble artificial materials from 'metamolecules,' which are manmade elementary building blocks," explained Eric Plum, a research lecturer at the University of Southampton's Optoelectronics Research Centre and Centre for Photonic Metamaterials.
"This provides a huge technological opportunity," Plum pointed out. "Instead of being limited by available natural materials, we can design materials with the properties we want. This has already led to the demonstration of various enhanced and novel material properties and functionalities."
Metamaterials appear homogenous to electromagnetic waves because their artificial structure is of subwavelength size--metamaterials for light are structured on the nanoscale, while those for microwaves are structured on the scale of millimeters or centimeters.
The group is interested in the twisted, or "chiral," structures found within many natural and artificial materials because they come with the ability to rotate the polarization state of transmitted light--a property known as optical activity. This property is the basis for applications ranging from LCD displays to spectroscopy, and even detection of life during space missions.
While the optical activity for light reflected by natural materials is negligible, the researchers found that the same isn't at all true for metamaterials.
"Our metamaterial exhibits huge optical activity for reflected electromagnetic waves," Plum said. "This is particularly remarkable considering that our artificial structure is extremely thin--30 times thinner than the wavelength of the electromagnetic radiation it manipulates."
Perhaps just as surprising, the optically active material involved isn't actually chiral. "Instead, optical activity arises from a chiral experimental arrangement associated with the mutual orientation of the direction of the illumination and the structure of the metamaterial, which lacks two-fold rotational symmetry," he elaborated.
The group's discovery paves the way for "a whole new class of extremely thin and light devices for controlling and detecting the polarization of light, such as polarization rotating and circularly polarizing beam splitters and mirrors, as well as optical isolators for circularly polarized light," Plum said.
In terms of more fundamental implications, the group's observed effect mimics the longitudinal magneto-optical Kerr effect--in which the light reflected from a magnetized surface can change in both reflected intensity and polarity - without a magnetized medium.
"This has significant implications for Kerr microscopy, because it could be mistaken for magnetization," he added.
Plum and colleagues are now busy developing practical solutions to enable dynamic control of specular optical activity for applications such as active polarization modulation.
"It would also be interesting to study the effect in natural materials and to explore the consequences of similar types of 'symmetry breaking' of other physical systems," Plum said.
####
About American Institute of Physics
pplied Physics Letters features concise, rapid reports on significant new findings in applied physics. The journal covers new experimental and theoretical research on applications of physics phenomena related to all branches of science, engineering, and modern technology. apl.aip.org
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
AIP Media Line
301-209-3090
Copyright © American Institute of Physics
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Tools
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
![]() Rice researchers harness gravity to create low-cost device for rapid cell analysis February 28th, 2025
Rice researchers harness gravity to create low-cost device for rapid cell analysis February 28th, 2025
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








