Home > Press > Wrinkles and crumples make graphene better
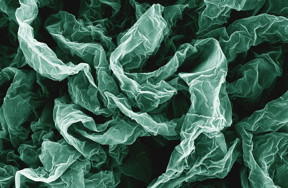 |
| Wrinkles and crumples, introduced by placing graphene on shrinky polymers, can enhance graphene's properties. CREDIT: Hurt and Wong Labs / Brown Unviversity |
Abstract:
Crumple a piece of paper and it's probably destined for the trash can, but new research shows that repeatedly crumpling sheets of the nanomaterial graphene can actually enhance some of its properties. In some cases, the more crumpled the better.
Wrinkles and crumples make graphene better
Providence, RI | Posted on March 22nd, 2016The research by engineers from Brown University shows that graphene, wrinkled and crumpled in a multi-step process, becomes significantly better at repelling water--a property that could be useful in making self-cleaning surfaces. Crumpled graphene also has enhanced electrochemical properties, which could make it more useful as electrodes in batteries and fuel cells.
The results are published in the journal Advanced Materials.
Generations of wrinkles
This new research builds on previous work done by Robert Hurt and Ian Wong, from Brown's School of Engineering. The team had previously showed that by introducing wrinkles into graphene, they could make substrates for culturing cells that were more similar to the complex environments in which cells grow in the body. For this latest work, the researchers led by Po-Yen Chen, a Hibbit postdoctoral fellow, wanted to build more complex architectures incorporating both wrinkles and crumples. "I wanted to see if there was a way to create higher-generational structures," Chen said.
To do that, the researchers deposited layers of graphene oxide onto shrink films--polymer membranes that shrink when heated (kids may know these as Shrinky Dinks). As the films shrink, the graphene on top is compressed, causing it to wrinkle and crumple. To see what kind of structures they could create, the researchers compressed same graphene sheets multiple times. After the first shrink, the film was dissolved away, and the graphene was placed in a new film to be shrunk again.
The researchers experimented with different configurations in the successive generations of shrinking. For example, sometimes they clamped opposite ends of the films, which caused them to shrink only along one axis. Clamped films yielded graphene sheets with periodic, basically parallel wrinkles across its surface. Unclamped films shrank in two dimensions, both length- and width-wise, creating a graphene surface that was crumpled in random shapes.
The team experimented with those different modes of shrinking over three successive generations. For example, they might shrink the same graphene sheet on a clamped film, then an unclamped film, then clamped again; or unclamped, clamped, unclamped. They also rotated the graphene in different configurations between shrinkings, sometimes placing the sheet perpendicular to its original orientation.
The team found that the multi-generational approach could substantially compress the graphene sheets, making them as small as one-fortieth their original size. They also showed that successive generations could create interesting patterns along the surface--wrinkles and crumples that were superimposed onto each other, for example.
"As you go deeper into the generations you tend to get larger wavelength structures with the original, smaller wavelength structure from earlier generations built into them," said Robert Hurt, a professor of engineering at Brown and one of the paper's corresponding authors.
A sheet that was shrunk clamped, unclamped, and then clamped looked different from ones that were unclamped, clamped, unclamped, for example.
"The sequence matters," said Wong, also a corresponding author on the paper. "It's not like multiplication where 2 times 3 is the same as 3 times 2. The material has a 'memory' and we get different results when we wrinkle or crumple in a different order."
The researchers generated a kind of taxonomy of structures born from different shrinking configurations. They then tested several of those structures to see how they altered the properties of the graphene sheets.
Enhanced properties
They showed that a highly crumpled graphene surface becomes superhydrophobic--able to resist wetting by water. When water touches a hydrophobic surface, it beads up and rolls off. When the contact angle of those water beads with an underlying surface exceeds 160 degrees--meaning very little of the water bead's surface touches the material--the material is said to be superhydrophobic. The researchers showed that they could make superhydrophobic graphene with three unclamped shrinks.
The team also showed that crumpling could enhance the electrochemical behaviors of graphene, which could be useful in next-generation energy storage and generation. The research showed that crumpled graphene used as a battery electrode had as much as a 400 percent increase in electrochemical current density over flat graphene sheets. That increase in current density could make for vastly more efficient batteries.
"You don't need a new material to do it," Chen said. "You just need to crumple the graphene."
In additional to batteries and water resistant coatings, graphene compressed in this manner might also be useful in stretchable electronics--a wearable sensor, for example.
The group plans to continue experimenting with different ways of generating structures on graphene and other nanomaterials.
"There are many new two-dimensional nanomaterials that have interesting properties, not just graphene," Wong said. "So other materials or combinations of materials may also organize into interesting structures with unexpected functionalities."
###
The work was supported by a seed grant from Brown University. Po-Yen Chen was supported by the Hibbit Engineering Fellows Program, which supports outstanding postdoctoral researchers as they transition to an independent career. Jaskiranjeet Sodhi, Dr. Yang Qiu, Thomas M. Valentin, Ruben Spitz Steinberg and Dr. Zhongying Wang were coauthors on the paper.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Kevin Stacey
401-863-3766
Copyright © Brown University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








