Home > Press > Researchers at the University of Gothenburg create focused spin wave beams: Synchronize an unlimited number of spintronic oscillators
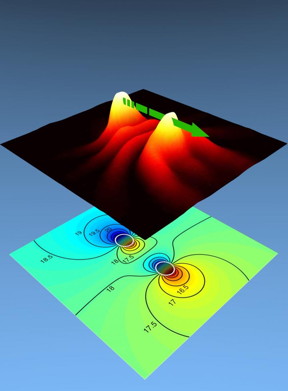 |
| Focused spin wave beams. CREDIT: University of Gothenburg |
Abstract:
Researchers at the University of Gothenburg Physics Department have finally found the secret to synchronize an unlimited number of spintronic oscillators. Such devices are very promising for future applications requiring wideband functionality.
Researchers at the University of Gothenburg create focused spin wave beams: Synchronize an unlimited number of spintronic oscillators
Gothenburg, Sweden | Posted on December 23rd, 2015Unfortunately, such nanoscale microwave oscillators suffer from an unbearably low power and high phase noise. It is generally accepted that one of the most attractive ways to solve this issue is to synchronize a large number of these nanoscopic oscillators in order to limit the detrimental influence of thermal energy.
The synchronization of two such oscillators was first published in 2005. However, by 2013 the number of synchronized oscillators had only increased to four low-frequency oscillators and three microwave-frequency oscillators. Furthermore, the coupling was difficult to control in a reproducible manner.
PhD student Afshin Houshang and his supervisor Dr. Randy Dumas in Professor Johan Åkerman's team have now succeeded in demonstrating that it is possible to create and utilize focused beams of spin waves to (i) synchronize oscillators over much larger distances than shown previously and (ii) robustly synchronize a record number of oscillators.
In their article, published in Nature Nanotechnology, they synchronize five oscillators and demonstrate the resulting improvement in the oscillator quality.
- Because we now know how to control the spin wave propagation, there is really no limit to how many oscillators we can now synchronize, said Randy Dumas, who sees great potential in several research areas.
Since the direction of the spin wave beam can also be tailored via electrical current through the oscillator and via an external magnetic field, the results will also have a major impact in the burgeoning field of spin wave based electronics, termed magnonics. By changing the direction of the beam, one can choose which oscillators synchronize and thereby control the flow of information in magnonic circuits in a way that was not possible before.
The results also open up new opportunities for fundamental studies of networks of strongly nonlinear oscillators where an array of perhaps a hundred such oscillators in different geometric architectures can be externally controlled and studied in detail.
- We hope to use these and similar components for extremely fast neuromorphic calculations based on oscillator networks explains Randy.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Johan Åkerman
46-707-104-360
Copyright © University of Gothenburg
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Spintronics
![]() Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








