Home > Press > Graphene displays clear prospects for flexible electronics
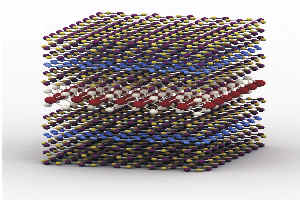 |
| LED Heterostructure Schematic |
Abstract:
Published in the scientific journal Nature Materials, University of Manchester and University of Sheffield researchers show that new 2D 'designer materials' can be produced to create flexible, see-through and more efficient electronic devices.
Graphene displays clear prospects for flexible electronics
Manchester, UK | Posted on February 2nd, 2015The team, led by Nobel Laureate Sir Kostya Novoselov, made the breakthrough by creating LEDs which were engineered on an atomic level.
The new research shows that graphene and related 2D materials could be utilised to create light emitting devices for the next-generation of mobile phones, tablets and televisions to make them incredibly thin, flexible, durable and even semi-transparent.
The LED device was constructed by combining different 2D crystals and emits light from across its whole surface. Being so thin, at only 10-40 atoms thick, these new components can form the basis for the first generation of semi-transparent smart devices.
One-atom thick graphene was first isolated and explored in 2004 at The University of Manchester. Its potential uses are vast but one of the first areas in which products are likely to be seen is in electronics. Other 2D materials, such as boron nitiride and molybdenum disulphide, have since been discovered opening up vast new areas of research and applications possibilities.
By building heterostructures - stacked layers of various 2D materials - to create bespoke functionality and introducing quantum wells to control the movement of electrons, new possibilities for graphene based optoelectronics have now been realised.
Freddie Withers, Royal Academy of Engineering Research Fellow at The University of Manchester, who led the production of the devices, said: "As our new type of LED's only consist of a few atomic layers of 2D materials they are flexible and transparent. We envisage a new generation of optoelectronic devices to stem from this work, from simple transparent lighting and lasers and to more complex applications."
Explaining the creation of the LED device Sir Kostya Novoselov said: "By preparing the heterostructures on elastic and transparent substrates, we show that they can provide the basis for flexible and semi-transparent electronics.
"The range of functionalities for the demonstrated heterostructures is expected to grow further on increasing the number of available 2D crystals and improving their electronic quality."
Prof Alexander Tartakovskii, from The University of Sheffield added: "The novel LED structures are robust and show no significant change in performance over many weeks of measurements.
"Despite the early days in the raw materials manufacture, the quantum efficiency (photons emitted per electron injected) is already comparable to organic LEDs."
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Ben Robinson
44-161-275-50134
Copyright © University of Manchester
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Flexible Electronics
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() Flexible electronics integrated with paper-thin structure for use in space January 17th, 2025
Flexible electronics integrated with paper-thin structure for use in space January 17th, 2025
Display technology/LEDs/SS Lighting/OLEDs
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Textiles/Clothing
![]() Protective equipment with graphene nanotubes meets the strictest ESD safety standards March 25th, 2022
Protective equipment with graphene nanotubes meets the strictest ESD safety standards March 25th, 2022
![]() Polymer fibers with graphene nanotubes make it possible to heat hard-to-reach, complex-shaped items February 11th, 2022
Polymer fibers with graphene nanotubes make it possible to heat hard-to-reach, complex-shaped items February 11th, 2022
![]() Flexible material shows potential for use in fabrics to heat, cool July 3rd, 2020
Flexible material shows potential for use in fabrics to heat, cool July 3rd, 2020
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Quantum nanoscience
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








