Home > Press > New method to generate arbitrary optical pulses
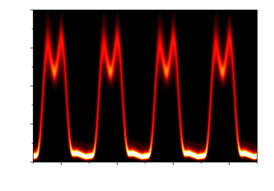 |
| This is an example of custom-shaped pulses at 100-GHz repetition rate.
CREDIT: University of Southampton |
Abstract:
Scientists from the University of Southampton have developed a new technique to generate more powerful, more energy efficient and low-cost pulsed lasers.
New method to generate arbitrary optical pulses
Southampton, UK | Posted on January 21st, 2015The technique, which was developed by researchers from the University's Optoelectronics Research Centre (ORC), has potential applications in a number of fields that use pulsed lasers including telecommunications, metrology, sensing and material processing.
Any application that requires optical pulses typically needs waveforms of a specific repetition rate, pulse duration, and pulse shape. It is often challenging to design and manufacture a laser with these parameters exactly as required. Even when a suitable solution exists, the size, the complexity and ease of operation of the laser are further critical considerations.
The new method works on a fundamentally different principle to existing pulsed lasers. It relies upon the coherent combination of multiple semiconductor lasers, each operating continuous-wave at different precisely defined frequencies (wavelengths). Through the precise control of the amplitude and phase of each laser's output, it is possible to produce complex pulsed optical waveforms with a huge degree of user flexibility. The key to making the approach work is to phase-lock the semiconductor lasers to an optical frequency comb, which ensures the individual lasers have well-defined mutual coherence.
David Wu, lead author of the study and winner of the 2014 Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC) ICT Pioneers award for this work, said: "As our new technique is based on a different approach to that currently used, it has several distinct features that are relevant in many applications. First, it is easily scalable - by combining a larger number of input lasers, shorter or more complicated-shape pulses and/or more power can be obtained. It can also generate pulses with a very low-level of noise (down to the quantum limit) and very high (greater than one THz) repetition frequencies.
"Finally, it consists of miniature and low-cost semiconductor lasers that can be all integrated on the same chip, making our pulse generator potentially very compact, robust, energetically efficient, and low-cost."
Dr Radan Slavik, who leads the research group, added: "We believe that this work is likely to be of direct interest to scientists working in virtually any field of optics where pulsed laser sources are used. We also believe that the concept and phase-locking technology developed could be widely applicable with the broader optics/photonics community."
###
The research is reported in a recent issue of the journal Optica - a new The Optical Society (OSA) journal, which focuses on rapid dissemination of high-impact results in all areas of optics and photonics (It is the first Southampton study to feature in Optica). The research is funded by the EPSRC through the Early Career Research Fellowship of Dr Slavik (EP/K003038/1) and through the "Photonic Hyperhighway" Programme Grant (EP/101196X).
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Glenn Harris
44-023-805-93212
Copyright © University of Southampton
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Wireless/telecommunications/RF/Antennas/Microwaves
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








