Home > Press > Scalable CVD process for making 2-D molybdenum diselenide: Rice, NTU scientists unveil CVD production for coveted 2-D semiconductor
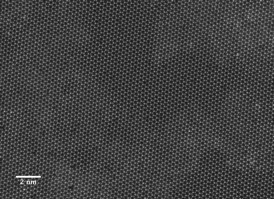 |
| This image from a scanning transmission electron microscope shows the individual atoms in a two-dimensional sheet of molybdenum diselenide. CREDIT: E. Ringe/Rice University |
Abstract:
Nanoengineering researchers at Rice University and Nanyang Technological University in Singapore have unveiled a potentially scalable method for making one-atom-thick layers of molybdenum diselenide -- a highly sought semiconductor that is similar to graphene but has better properties for making certain electronic devices like switchable transistors and light-emitting diodes.
Scalable CVD process for making 2-D molybdenum diselenide: Rice, NTU scientists unveil CVD production for coveted 2-D semiconductor
Houston, TX | Posted on April 8th, 2014The method for making two-dimensional molybdenum diselenide uses a technique known as chemical vapor deposition (CVD) and is described online in a new paper in the American Chemical Society journal ACS Nano. The finding is significant because CVD is widely used by the semiconductor and materials industries to make thin films of silicon, carbon fibers and other materials.
"This new method will allow us to exploit the properties of molybdenum diselenide in a number of applications," said study leader Pulickel Ajayan, chair of Rice's Department of Materials Science and NanoEngineering. "Unlike graphene, which can now easily be made in large sheets, many interesting 2-D materials remain difficult to synthesize. Now that we have a stable, efficient way to produce 2-D molybdenum diselenide, we are planning to expand this robust procedure to other 2-D materials."
In the Rice study, Ajayan and colleagues tested their atomically thin layers of molybdenum diselenide by building a field effect transistor (FET), a commonly used device in the microelectronic industry. Tests of the FET found the electronic properties of the molybdenum diselenide layers were significantly better than those of molybdenum disulfide; the latter is a similar material that has been more extensively studied because it was easier to fabricate. For example, the FET tests found that the electron mobility of Rice's molybdenum diselenide was higher than that of CVD-grown, molybdenum disulfide.
In solid-state physics, electron mobility refers to how quickly electrons pass through a metal or semiconductor in the presence of an electric field. Materials with high electron mobility are often preferred to reduce power consumption and heating in microelectronic devices.
"Being able to make 2-D materials in a controlled fashion really will make an impact on our understanding and use of their fascinating properties," said study co-author Emilie Ringe, assistant professor of materials science and nanoengineering and of chemistry at Rice. "Characterizing both the structure and function of a material, as we have done in this paper, is critical to such advances."
Molybdenum diselenide and molybdenum disulfide each belong to a class of materials known as transition metal dichalcogenides; TMDCs are so named because they consist of two elements, a transition metal like molybdenum or tungsten and a "chalcogen" like sulfur, selenium or tellurium.
TMDCs have attracted intense interest from materials scientists because they have an atomic structure similar to graphene, the pure carbon wonder materials that attracted the 2010 Nobel Prize in physics. Graphene and similar materials are often referred to as two-dimensional because they are only one atom thick. Graphene has extraordinary electronic properties. For example, its electron mobility is tens of thousands of times greater than that of TMDCs.
However, two-dimensional TMDCs like molybdenum diselenide have attracted intense interest because their electronic properties are complementary to graphene. For example, pure graphene has no bandgap -- a useful electronic property that engineers can exploit to make FETs that are easily switched on and off.
As with many nanomaterials, scientists have found that the physical properties of TMDCs change markedly when the material has nanoscale properties. For example, a slab of molybdenum diselenide that is even a micron thick has an "indirect" bandgap while a two-dimensional sheet of molybdenum diselenide has a "direct" bandgap. The difference is important for electronics because direct-bandgap materials can be used to make switchable transistors and sensitive photodetectors.
"One of the driving forces in Rice's Department of Materials Science and NanoEngineering is the close collaborations that develop between the people who are focused on synthesis and those of us involved with characterization," said Ringe, who joined Rice's faculty in January. "We hope this will be the beginning of a series of new protocols to reliably synthesize a variety of 2-D materials."
The research was supported by the Army Research Office, the Semiconductor Research Corporation's FAME Center, the Office of Naval Research and Singapore's MOE Academic Research Fund.
Additional study co-authors include Xingli Wang, Yongji Gong, Gang Shi, Kunttal Keyshar, Gonglan Ye, Robert Vajtai and Jun Lou, all of Rice, and Wai Leong Chow, Zheng Liu and Beng Kang Tay, all of Nanyang Technological University.
####
About Rice University
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation's top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is home to the Baker Institute for Public Policy. With 3,920 undergraduates and 2,567 graduate students, Rice's undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is 6.3-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice has been ranked No. 1 for best quality of life multiple times by the Princeton Review and No. 2 for "best value" among private universities by Kiplinger's Personal Finance.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Jade Boyd
713-348-6778
Copyright © Rice University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() A copy of the ACS Nano paper is available at:
A copy of the ACS Nano paper is available at:
![]() More information about Rice's Department of Materials Science and NanoEngineering:
More information about Rice's Department of Materials Science and NanoEngineering:
| Related News Press |
Thin films
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Display technology/LEDs/SS Lighting/OLEDs
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








