Home > Press > Brighter inks, without pigment: Nanostructured capsules could bring about paints and electronic displays that never fade
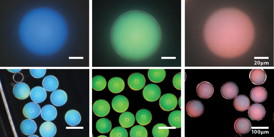 |
| These photonic microcapsules have been prepared to produce blue, green, and red structural colors and imaged using bright-field (top) and dark-field (bottom) optical microscopy. Images courtesy of Jin-Gyu Park. |
Abstract:
Among the taxidermal specimens in Harvard's Museum of Comparative Zoology, past centuries-old fur coats, arises a flicker of brilliant blue. This is the spangled cotinga. Surprisingly, the cotinga is about as old as everything in the room, but its color is still as dazzling as the day it was brought to the museum. The cotinga—or rather its feathers—achieve this effect through structural color.
Brighter inks, without pigment: Nanostructured capsules could bring about paints and electronic displays that never fade
Cambridge, MA | Posted on March 14th, 2014Unlike color that we usually think of, which arises from paints and dyes absorbing certain wavelengths of light and reflecting the remainder, structural color is created when an object's very nanostructure amplifies a specific wavelength. Cells in the cotinga's feathers have a series of tiny pores spaced just right so that blues (and not much of anything else) are reflected back to our eyes. Because of this, if the feathers were thoroughly pulverized, the formation of pores and therefore the color would be lost. It also means that the same color could be produced from an entirely different material, if one could recreate the same pattern made by the feathers' pores.
Researchers led by Vinothan N. Manoharan at the Harvard School of Engineering and Applied Sciences want to recreate this effect, giving man-made materials structural color. Producing structural color is not easy, though; it often requires a material's molecules to be in a very specific crystalline pattern, like the natural structure of an opal, which reflects a wide array of colors. But the pores on the cotinga's feathers lack a regular order and are therefore a prime target for imitation.
Manoharan's lab has devised a system where microcapsules are filled with a disordered solution of even smaller particles suspended in water. When the microcapsule is partly dried out, it shrinks, bringing the particles closer and closer together. Eventually the average distance between all the particles will give rise to a specific reflected color from the capsule. Shrink the capsule a bit more, and they become another color, and then another.
"There's an average distance between particles, even though there is no ordering in the particles. It's that average distance that is important in determining the color," says Manoharan, Gordon McKay Professor of Chemical Engineering and Professor of Physics at Harvard.
The current project expands on research conducted at Yale University in 2009, which aimed to mimic the cotinga's hue and showed that dried aggregates of solid particles could create blues. Jin-Gyu Park was a postdoctoral researcher there and is now a research associate in Manoharan's group at Harvard SEAS, which specializes in the physics of colloidal suspensions. With Park as lead author, the new paper demonstrates the production of colors across the spectrum, and the new encapsulation system.
The tunable color capsules present interesting technological opportunities, says Manoharan. For example, a whole spectrum of new paints might be created using suspended capsules.
"Right now, the red dye carmine comes from an insect called a cochineal," says Manoharan. "People would like to move away from that because it's very labor-intensive, and getting that color involves harvesting a lot of insects."
Rather than harvesting from nature or preparing specialty chemicals, one for each color, these capsules could provide a universal and direct path to any desired color.
The capsules might also offer a safety advantage. The reason for using natural dyes like carmine is that many synthetic dyes are toxic. The new color capsules can be made with particles of almost any material in the right structural formation, so toxicity can be easily avoided.
Most compelling of all, however, is that some structural colors found in nature can last indefinitely as long as the colored object remains intact.
"Most color you get in paints, coatings or cosmetics, even, comes from the selective absorption and reflection of light. What that means is that the material is absorbing some energy, and that means that over time, the material will fade," says Manoharan.
The sun's energy pummels the molecules in conventional pigments. Eventually, the molecules simply deteriorate and no longer absorb the colors they used to, leading to sun bleaching. Manoharan's group is currently testing their innovation to see if it can create an effectively ageless color.
Electronic display technology—for example, e-readers—might also benefit from this advance. The microcapsules could be used in displays that create pixels with colored particles rather than LEDs, liquid crystals, or black-and-white "electronic ink."
"We think it could be possible to create a full-color display that won't fade over time," says Manoharan. "The dream is that you could have a piece of flexible plastic that you can put graphics on in full color and read in bright sunlight."
The Harvard Office of Technology Development has filed a provisional patent and is working with Manoharan's lab to pursue the commercialization of the color capsule technology.
Manoharan's and Park's coauthors were Sofia Magkiriadou, a Ph.D. student in physics at the Harvard Graduate School of Arts and Sciences; Shin-Hyun Kim and Tae Min Choi at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology; and Young-Seok Kim at Korea Electronics Technology Institute.
This research was supported by an International Collaboration grant from the Ministry of Trade, Industry & Energy of Korea, and by the Harvard Materials Research Science and Engineering Center through the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF). The work was performed in part at the NSF-supported Center for Nanoscale Systems at Harvard University.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Paul Karoff
617-496-0450
Copyright © Harvard University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() The findings have been published in the journal Angewandte Chemie:
The findings have been published in the journal Angewandte Chemie:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Display technology/LEDs/SS Lighting/OLEDs
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Efficient and stable hybrid perovskite-organic light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40 per cent July 5th, 2024
Efficient and stable hybrid perovskite-organic light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40 per cent July 5th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Home
![]() Nanomaterials enable dual-mode heating and cooling device: Device could cut HVAC energy use by nearly 20% in the US December 2nd, 2020
Nanomaterials enable dual-mode heating and cooling device: Device could cut HVAC energy use by nearly 20% in the US December 2nd, 2020
![]() Bosch Sensortec launches ideation community to foster and accelerate innovative IoT applications : Creativity hub for customers, partners, developers and makers February 18th, 2019
Bosch Sensortec launches ideation community to foster and accelerate innovative IoT applications : Creativity hub for customers, partners, developers and makers February 18th, 2019
![]() Iran Develops Water-Repellent Nano-Paint December 5th, 2018
Iran Develops Water-Repellent Nano-Paint December 5th, 2018
Industrial
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Quantum interference in molecule-surface collisions February 28th, 2025
Quantum interference in molecule-surface collisions February 28th, 2025
![]() Boron nitride nanotube fibers get real: Rice lab creates first heat-tolerant, stable fibers from wet-spinning process June 24th, 2022
Boron nitride nanotube fibers get real: Rice lab creates first heat-tolerant, stable fibers from wet-spinning process June 24th, 2022
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








