Home > Press > Domain walls as new information storage medium - Visualization of domain wall motion: Material defects do not impede wall motion at high velocities / Publication of findings in Nature Communications 23
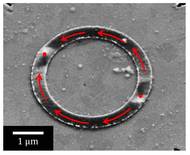 |
| Image of a ferromagnetic ring prepared using a scanning electron microscope: The magnetization (black/white contrast) runs along the ring and forms two domain walls. |
Abstract:
While searching for ever smaller devices that can be used as data storage systems and novel sensors, physicists at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU) have directly observed magnetization dynamics processes in magnetic nanowires and thus paved the way for further research in the field of nanomagnetism. Small magnetic domain wall structures in nanowires can be used to store information and, for example, can be used as angle sensors. Initial applications based on magnetic domain walls have been developed and are already in use in sensor technology. The current findings represent the first experimentally recorded direct imaging of predicted correlations between magnetic spin structure and wall velocity. The newly discovered properties could be used for other future applications in information technology.
Domain walls as new information storage medium - Visualization of domain wall motion: Material defects do not impede wall motion at high velocities / Publication of findings in Nature Communications 23
Mainz, Germany | Posted on September 23rd, 2013 Magnetic domains represent regions of uniform magnetization in ferromagnetic materials. Within each domain, the magnetization is aligned in a single direction. At the interface where domains of different magnetization direction meet, the magnetization has to rotate from one direction to another in a so-called domain wall. At Mainz University, the group of Professor Mathias Kläui is studying the properties of magnetic domains and the dynamics of domains and domain walls in tiny rings on the nanoscale. It is possible to directly observe the motion of domain walls in these rings that have a diameter of some 4 micrometers and are made of permalloy, a soft nickel-iron alloy. For this purpose, the Mainz physicists have been collaborating with scientists of the BESSY II synchrotron facility at the Helmholtz Center Berlin for Materials and Energy and the Advanced Light Source (ALS) at the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Berkeley, USA, as well as with the Technical University of Berlin and the Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems in Stuttgart.
The researchers discovered that the velocity of the motion of domain walls is always oscillating. "This is a new effect that could prove to be useful in the future," said Dr. André Bisig, lead author of the paper "Correlation between spin structure oscillations and domain wall velocities," which has recently been published in Nature Communications. It was also found that the applied method is very effective in reliably moving the domain walls at very high velocities. "The faster we move the domain wall, the easier it is to control it," said Bisig. Another observation concerns the effects associated with irregularities or defects in the nanowires. According to the results, these effects only become noticeable when domain walls are moving slowly. The faster a domain wall spins, the less relevant is the role played by defects in the material.
While theoretical research concerns itself principally with observing domain wall velocity and its correlation with oscillations in the spin structure, the results obtained also have important implications for applied research. Domain wall-based sensors are already being used by Sensitec GmbH, Mainz, a cooperating partner of JGU and the Technical University of Kaiserslautern in two projects funded by the state of Rhineland-Palatinate: the Spintronics Technology Platform in Rhineland-Palatinate (STeP) and the Technology Transfer Service Center for New Materials (TT-DINEMA). "Of particular importance is the fact that we observed unimpeded domain wall motion at high domain wall velocities. This represents highly promising potential for the use of these nanostructures in ultra-fast rotating sensors," added Professor Mathias Kläui. The research being undertaken by Professor Kläui's team is being funded by an ERC Starting Grant and the Graduate School of Excellence Materials Science in Mainz (MAINZ). In addition, cooperation with Sensitec has resulted in access to a joint EU project involving seven other leading partners expected to start in October 2013 on "Controlling domain wall dynamics for functional devices".
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Dr. André Bisig
Condensed Matter Physics (KOMET)
Institute of Physics
Johannes Gutenberg University
D 55099 Mainz
Tel +49 6131 39-23635
Fax +49 6131 39-24076
Copyright © Johannes Gutenberg Universitaet Mainz
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Spintronics
![]() Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Memory Technology
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








