Home > Press > Study suggests second life for possible spintronic materials: Ohio University research merges manganese, gallium nitride in uniform layer
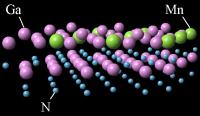 |
| This image shows a 3-D rendering of a stable manganese gallium nitride surface structure.
Credit: A.R. Smith, Ohio University |
Abstract:
Ten years ago, scientists were convinced that a combination of manganese and gallium nitride could be a key material to create spintronics, the next generation of electronic devices that operate on properties found at the nanoscale. But researchers grew discouraged when experiments indicated that the two materials were as harmonious as oil and water.
Study suggests second life for possible spintronic materials: Ohio University research merges manganese, gallium nitride in uniform layer
Athens, OH | Posted on June 6th, 2013A new study led by Ohio University physicists suggests that scientists should take another look at this materials duo, which once was heralded for its potential to be the building block for devices that can function at or above room temperature.
"We've found a way—at least on the surface of the material—of incorporating a uniform layer," said Arthur Smith, a professor of physics and astronomy at Ohio University who leads the international collaboration of Argentinian and Spanish researchers.
The scientists made two important changes to create the material merger, they report in the journal Physical Review B. First, they used the nitrogen polarity of gallium nitride, whereas conventional experiments used the gallium polarity to attach to the manganese, Smith explained. Second, they heated the sample.
At lower temperatures (less than 105 degrees Celsius), the manganese atoms "float" on the outer layer of gallium atoms. When the scientists raised the temperature about 100 degrees Celsius, Smith said, the atoms connected to the nitrogen layer underneath, creating a manganese-nitrogen bond. This bond remains stable, even at very high temperatures.
The theoretical scientists accurately predicted that a "triplet" structure of three manganese atoms would form a metastable structure at low temperatures, Smith said. But at higher temperatures, those manganese atoms break apart and bond with nitrogen. Valeria Ferrari of the Centro Atómico Constituyentes said her group performed quantum mechanical simulations to test which model structures have the lowest energy, which suggested both the trimer structure and the manganese-nitrogen bonded structure.
Now that scientists have shown that they can create a stable structure with these materials, they will investigate whether it has the magnetic properties at room temperature necessary to function as a spintronic material.
###
The study authors are Abhijit Chinchore, Kangkang Wang, Meng Shi, Andrada Mandru, Yinghao Liu, Muhammad Haider and Arthur Smith of the Nanoscale and Quantum Phenomena Institute at Ohio University; Valeria Ferrari and Maria Andrea Barral of the Centro Atómico Constituyentes, GIyA, CNEA, San Martín, Buenos Aires, Argentina; and Pablo Ordejón, Centre d'Investigació en Nanociència i Nanotecnologia, Barcelona, Spain.
The research was supported by the U.S. Department of Energy, Office of Basic Energy Sciences, Division of Materials Sciences and Engineering (STM studies of nanoscale spintronic nitride systems), the National Science Foundation (advancing nanospintronics through international collaboration), CONICET, ANPCyT and Spanish MICINN. The Ohio Supercomputing Center provided computer time.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Arthur Smith
(740) 597-2576
Andrea Gibson
(740) 597-2166
Copyright © Ohio University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Spintronics
![]() Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
Quantum nanoscience
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








