Home > Press > Machine learning peeks into nano-aquariums
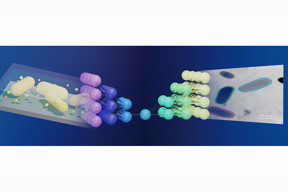 |
| Illinois researchers have linked electron microscope imaging and machine learning, making it much easier to study nanoparticles in action. The schematic shows how a neural network, middle, works as a bridge between liquid-phase electron microscope imaging, left, and streamlined data output, right. For more information visit, pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acscentsci.0c00430. Graphic courtesy ACS and the Qian Chen group |
Abstract:
In the nanoworld, tiny particles such as proteins appear to dance as they transform and assemble to perform various tasks while suspended in a liquid. Recently developed methods have made it possible to watch and record these otherwise-elusive tiny motions, and researchers now take a step forward by developing a machine learning workflow to streamline the process.
Machine learning peeks into nano-aquariums
Champaign, IL | Posted on August 31st, 2020The new study, led by Qian Chen, a professor of materials science and engineering at the University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign, builds upon her past work with liquid-phase electron microscopy and is published in the journal ACS Central Science.
Being able to see – and record – the motions of nanoparticles is essential for understanding a variety of engineering challenges. Liquid-phase electron microscopy, which allows researchers to watch nanoparticles interact inside tiny aquariumlike sample containers, is useful for research in medicine, energy and environmental sustainability and in fabrication of metamaterials, to name a few. However, it is difficult to interpret the dataset, the researchers said. The video files produced are large, filled with temporal and spatial information, and are noisy due to background signals – in other words, they require a lot of tedious image processing and analysis.
“Developing a method even to see these particles was a huge challenge,” Chen said. “Figuring out how to efficiently get the useful data pieces from a sea of outliers and noise has become the new challenge.”
To confront this problem, the team developed a machine learning workflow that is based upon an artificial neural network that mimics, in part, the learning potency of the human brain. The program builds off of an existing neural network, known as U-Net, that does not require handcrafted features or predetermined input and has yielded significant breakthroughs in identifying irregular cellular features using other types of microscopy, the study reports.
“Our new program processed information for three types of nanoscale dynamics including motion, chemical reaction and self-assembly of nanoparticles,” said lead author and graduate student Lehan Yao. “These represent the scenarios and challenges we have encountered in the analysis of liquid-phase electron microscopy videos.”
The researchers collected measurements from approximately 300,000 pairs of interacting nanoparticles, the study reports.
Click here to see liquid-phase electron microscopy with combined machine learning in action.
As found in past studies by Chen’s group, contrast continues to be a problem while imaging certain types of nanoparticles. In their experimental work, the team used particles made out of gold, which is easy to see with an electron microscope. However, particles with lower elemental or molecular weights like proteins, plastic polymers and other organic nanoparticles show very low contrast when viewed under an electron beam, Chen said.
“Biological applications, like the search for vaccines and drugs, underscore the urgency in our push to have our technique available for imaging biomolecules,“ she said. “There are critical nanoscale interactions between viruses and our immune systems, between the drugs and the immune system, and between the drug and the virus itself that must be understood. The fact that our new processing method allows us to extract information from samples as demonstrated here gets us ready for the next step of application and model systems.”
The team has made the source code for the machine learning program used in this study publicly available through the supplemental information section of the new paper. “We feel that making the code available to other researchers can benefit the whole nanomaterials research community,”Chen said.
Chen also is affiliated with chemistry, the Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology and the Materials Research Laboratory at the U. of I.
The National Science Foundation and Air Force Office of Scientific Research supported this study.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Qian Chen
217-300-1137
Copyright © University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Nanofabrication
![]() Self-propelled protein-based nanomotors for enhanced cancer therapy by inducing ferroptosis June 6th, 2025
Self-propelled protein-based nanomotors for enhanced cancer therapy by inducing ferroptosis June 6th, 2025
![]() Multiphoton polymerization: A promising technology for precision medicine February 28th, 2025
Multiphoton polymerization: A promising technology for precision medicine February 28th, 2025
![]() New chip opens door to AI computing at light speed February 16th, 2024
New chip opens door to AI computing at light speed February 16th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








