Home > Press > Highly sensitive dopamine detector uses 2D materials
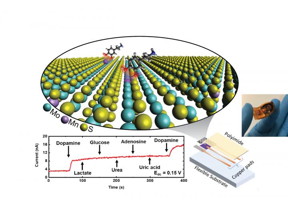 |
| Schematic of a highly selective dopamine detector using two-dimensional material. CREDIT Derrick Butler, Penn State |
Abstract:
A supersensitive dopamine detector can help in the early diagnosis of several disorders that result in too much or too little dopamine, according to a group led by Penn State and including Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute and universities in China and Japan.
Highly sensitive dopamine detector uses 2D materials
University Park, PA | Posted on August 7th, 2020Dopamine is an important neurotransmitter that can be used to diagnose disorders such as Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease and schizophrenia.
"If you can develop a very sensitive, yet simple-to-use and portable, detector that can identify a wide range of dopamine concentration, for instance in sweat, that could help in non-invasive monitoring of an individual's health," said Aida Ebrahimi, assistant professor of electrical engineering, Penn State, and a corresponding author on a paper published Aug. 7 in Science Advances.
Their work shows that by adding a small amount of manganese to a two-dimensional layered material called molybdenum disulfide, they can improve the sensitivity by many orders of magnitude compared to other reported results, while also achieving high specificity. Importantly, their detector is low-cost and flexible, and can detect dopamine in background media including buffer, serum and sweat, and in real-time.
"Regarding our method, electrochemical deposition is a new way of depositing these chemicals that is very simple and scalable," said Mauricio Terrones, Verne M. Willaman Professor of Physics, Materials Science and Chemistry and the second corresponding author. "The air force is interested in these neurotransmitters that are makers of stress. I envision this as a wearable sensor."
Humberto Terrones and his group, at RPI, performed the computational investigation that allowed them to explain how addition of manganese results in an improved response to dopamine. The experimental work was performed within the Center for Atomically Thin Multifunctional Coatings (ATOMIC) at Penn State.
"Combining the experimental results with computational studies proved to be very insightful, and I think we all learned much more throughout this project because of that," said Derrick Butler, a co-lead author on the paper and doctoral student at Penn State. "Developing these materials and applying them in a way that could improve the health and well-being of others makes the work especially enjoyable and rewarding."
His co-lead author, doctoral candidate Yu Lei, added, "One challenge is to develop a scalable method to bridge fundamental studies and practical applications. Our method is based on electrodeposition, which has been widely used in industry, thus providing a scalable route to functionalize MoS2 in a scalable way. Also, I believe this multidisciplinary team is the key to find the right way to functionalize MoS2 for ultrasensitive dopamine detection."
In further work, the group hopes to find other material combinations to detect a variety of other biomarkers with the specificity of their current sensor. Creating such a "toolkit" combining experimental investigations with computational methods will lead to new materials with multifunctional capabilities. This might be useful beyond human health, for example, for detecting noxious gases, water contamination or biodefense agents.
"In future, we can envision a combined sensor/actuator that can detect the dopamine and provide therapy at the same time. The sensors can be integrated with miniaturized chips for integration of sensing, actuating, control and data processing," Ebrahimi said.
###
In addition to Ebrahimi, Lei, Butler and the Terrones brothers, authors include Fu Zhang and Tomotaroh Granzier-Nakajiwa, former or current doctoral students at Penn State, and Kazinora Fujisawa, currently a post-doctoral scholar, Penn State. Their paper is titled "Single-Atom Doping of MoS2 with Manganese Enables Ultrasensitive Detection of Dopamine: Experimental and Computational Approach."
National Science Foundation, IUCRC-ATOMIC Center and Ebrahimi's Start-up fund provided support for this project.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
A'ndrea Elyse Messer
814-865-5689
@penn_state
Terrones can be contacted at
Ebrahimi can be contacted at
Copyright © Penn State
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
2 Dimensional Materials
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() Closing the gaps — MXene-coating filters can enhance performance and reusability February 28th, 2025
Closing the gaps — MXene-coating filters can enhance performance and reusability February 28th, 2025
Wearable electronics
![]() Breakthrough brings body-heat powered wearable devices closer to reality December 13th, 2024
Breakthrough brings body-heat powered wearable devices closer to reality December 13th, 2024
![]() Beyond wires: Bubble technology powers next-generation electronics:New laser-based bubble printing technique creates ultra-flexible liquid metal circuits November 8th, 2024
Beyond wires: Bubble technology powers next-generation electronics:New laser-based bubble printing technique creates ultra-flexible liquid metal circuits November 8th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Homeland Security
![]() The picture of health: Virginia Tech researchers enhance bioimaging and sensing with quantum photonics June 30th, 2023
The picture of health: Virginia Tech researchers enhance bioimaging and sensing with quantum photonics June 30th, 2023
![]() Sensors developed at URI can identify threats at the molecular level: More sensitive than a dog's nose and the sensors don't get tired May 21st, 2021
Sensors developed at URI can identify threats at the molecular level: More sensitive than a dog's nose and the sensors don't get tired May 21st, 2021
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Environment
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








