Home > Press > Breaking through the limits of stretchable semiconductors with molecular brakes that harness light
 |
| Research Image CREDIT POSTECH |
Abstract:
Like the brakes that stop cars, a molecular brake exists that can prevent semiconductor chains from slipping, enabling the creation of more groundbreaking devices. Recently, a joint research team led by Professor Kilwon Cho and PhD candidates Seung Hyun Kim and Sein Chung from the Department of Chemical Engineering at POSTECH, and Professor Boseok Kang from the Department of Nano Engineering at Sungkyunkwan University (SKKU) has developed a technology for high-performance organic polymer semiconductors that exhibit both stretchability and electrical functionality. This study was recently featured on the inside back cover of Advanced Functional Materials.
Breaking through the limits of stretchable semiconductors with molecular brakes that harness light
Pohang, South Korea | Posted on June 9th, 2023For semiconductors to find applications in diverse flexible devices like flexible displays and skin-attachable medical devices, it is necessary to use stretchable materials instead of rigid ones. However, the force exerted during the stretching of semiconductors can be up to ten times greater than that experienced during simple bending, leading to the breakdown of the semiconductor layers and a decline in their electrical performance. Researchers have been diligently exploring methods to preserve semiconductor performance even under deformation, but a definitive solution to this challenge remains elusive.
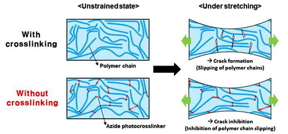
The research team successfully created a flexible molecular photocrosslinker1 featuring azide-reactive groups at both ends. When exposed to ultraviolet light, this photocrosslinker forms a network structure with the polymer semiconductor, acting as a brake that prevents slipping even under stretching conditions. In contrast to conventional semiconductor materials, where polymer chains become intertwined and irreversibly slip and fracture when stretched, the presence of this "brake" allows the polymer chains to retain their stretchability and performance without any slipping.
Using this approach, the research team successfully preserved up to 96 percent of the electrical performance of the polymer semiconductor, even when it was stretched to 80 percent. Moreover, the semiconductor exhibited significantly enhanced stretchability and durability compared to conventional semiconductors, clearly demonstrating the effectiveness of the developed technology.
Professor Kilwon Cho explained, "By incorporating azide photocrosslinkers into the films, we have successfully preserved the excellent electrical properties of polymer semiconductors for organic thin-film transistors even under significant mechanical deformation. This simple approach significantly enhances the stretchability and UV-patternability of organic semiconducting polymers, making it highly valuable for industries requiring large-area production and photolithography for the development of next-generation flexible electronics."
This study was conducted with the support of the Mid-career Researcher Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea and the Strategic Reinforcement of International Cooperation Network of the Ministry of Science and ICT of Korea.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Jinyoung Huh
Pohang University of Science & Technology (POSTECH)
Office: 82-54-279-2415
Copyright © Pohang University of Science & Technology (POSTECH)
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() New organic molecule shatters phosphorescence efficiency records and paves way for rare metal-free applications July 5th, 2024
New organic molecule shatters phosphorescence efficiency records and paves way for rare metal-free applications July 5th, 2024
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() New method cracked for high-capacity, secure quantum communication July 5th, 2024
New method cracked for high-capacity, secure quantum communication July 5th, 2024
![]() Searching for dark matter with the coldest quantum detectors in the world July 5th, 2024
Searching for dark matter with the coldest quantum detectors in the world July 5th, 2024
Flexible Electronics
![]() CityU awarded invention: Soft, ultrathin photonic material cools down wearable electronic devices June 30th, 2023
CityU awarded invention: Soft, ultrathin photonic material cools down wearable electronic devices June 30th, 2023
![]() Liquid metal sticks to surfaces without a binding agent June 9th, 2023
Liquid metal sticks to surfaces without a binding agent June 9th, 2023
Wearable electronics
![]() CityU awarded invention: Soft, ultrathin photonic material cools down wearable electronic devices June 30th, 2023
CityU awarded invention: Soft, ultrathin photonic material cools down wearable electronic devices June 30th, 2023
![]() Liquid metal sticks to surfaces without a binding agent June 9th, 2023
Liquid metal sticks to surfaces without a binding agent June 9th, 2023
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() Atomic force microscopy in 3D July 5th, 2024
Atomic force microscopy in 3D July 5th, 2024
![]() Aston University researcher receives £1 million grant to revolutionize miniature optical devices May 17th, 2024
Aston University researcher receives £1 million grant to revolutionize miniature optical devices May 17th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() New method cracked for high-capacity, secure quantum communication July 5th, 2024
New method cracked for high-capacity, secure quantum communication July 5th, 2024
![]() Searching for dark matter with the coldest quantum detectors in the world July 5th, 2024
Searching for dark matter with the coldest quantum detectors in the world July 5th, 2024
![]() Atomic force microscopy in 3D July 5th, 2024
Atomic force microscopy in 3D July 5th, 2024
Chip Technology
![]() New method cracked for high-capacity, secure quantum communication July 5th, 2024
New method cracked for high-capacity, secure quantum communication July 5th, 2024
![]() Diamond glitter: A play of colors with artificial DNA crystals May 17th, 2024
Diamond glitter: A play of colors with artificial DNA crystals May 17th, 2024
![]() Oscillating paramagnetic Meissner effect and Berezinskii-Kosterlitz-Thouless transition in cuprate superconductor May 17th, 2024
Oscillating paramagnetic Meissner effect and Berezinskii-Kosterlitz-Thouless transition in cuprate superconductor May 17th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Efficient and stable hybrid perovskite-organic light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40 per cent July 5th, 2024
Efficient and stable hybrid perovskite-organic light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40 per cent July 5th, 2024
![]() A New Blue: Mysterious origin of the ribbontail ray’s electric blue spots revealed July 5th, 2024
A New Blue: Mysterious origin of the ribbontail ray’s electric blue spots revealed July 5th, 2024
![]() New organic molecule shatters phosphorescence efficiency records and paves way for rare metal-free applications July 5th, 2024
New organic molecule shatters phosphorescence efficiency records and paves way for rare metal-free applications July 5th, 2024
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() New organic molecule shatters phosphorescence efficiency records and paves way for rare metal-free applications July 5th, 2024
New organic molecule shatters phosphorescence efficiency records and paves way for rare metal-free applications July 5th, 2024
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() New method cracked for high-capacity, secure quantum communication July 5th, 2024
New method cracked for high-capacity, secure quantum communication July 5th, 2024
![]() Searching for dark matter with the coldest quantum detectors in the world July 5th, 2024
Searching for dark matter with the coldest quantum detectors in the world July 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() New method cracked for high-capacity, secure quantum communication July 5th, 2024
New method cracked for high-capacity, secure quantum communication July 5th, 2024
![]() Searching for dark matter with the coldest quantum detectors in the world July 5th, 2024
Searching for dark matter with the coldest quantum detectors in the world July 5th, 2024
![]() Atomic force microscopy in 3D July 5th, 2024
Atomic force microscopy in 3D July 5th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








