Home > Press > Self-powered X-ray detector to revolutionize imaging for medicine, security and research: 2D perovskite thin films boost sensitivity 100-fold compared to conventional detectors, require no outside power source, and enable low-dose dental and medical images
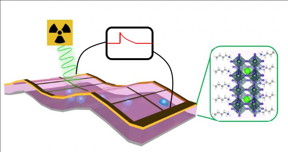 |
| X-ray detectors made with 2-dimensional perovskite thin films convert X-ray photons to electrical signals without requiring an outside power source, and are a hundred times more sensitive than conventional detectors. CREDIT Los Alamos National Laboratory |
Abstract:
A new X-ray detector prototype is on the brink of revolutionizing medical imaging, with dramatic reduction in radiation exposure and the associated health risks, while also boosting resolution in security scanners and research applications, thanks to a collaboration between Los Alamos National Laboratory and Argonne National Laboratory researchers.
Self-powered X-ray detector to revolutionize imaging for medicine, security and research: 2D perovskite thin films boost sensitivity 100-fold compared to conventional detectors, require no outside power source, and enable low-dose dental and medical images
Los Alamos, NM | Posted on April 12th, 2020"The perovskite material at the heart of our detector prototype can be produced with low-cost fabrication techniques," said Hsinhan (Dave) Tsai, an Oppenheimer Postdoctoral fellow at Los Alamos National Laboratory. "The result is a cost-effective, highly sensitive, and self-powered detector that could radically improve existing X-ray detectors, and potentially lead to a host of unforeseen applications."
The detector replaces silicon-based technology with a structure built around a thin film of the mineral perovskite, resulting in a hundred times more sensitivity than conventional silicon-based detectors. In addition, the new perovskite detector does not require an outside power source to produce electrical signals in response to X-rays.
High sensitivity perovskite detectors could enable dental and medical images that require a tiny fraction of the exposure that accompanies conventional X-ray imaging. Reduced exposure decreases risks for patients and medical staff alike. The fact that perovskite detectors can be made very thin allows them to offer increased resolution for highly detailed images, which will lead to improved medical evaluations and diagnoses. Lower-energy and increased-resolution detectors could also revolutionize security scanners and imaging in X-ray research applications.
Because perovskite is rich in heavy elements, such as lead and iodine, X-rays that easily pass through silicon undetected are more readily absorbed, and detected, in perovskite. As a result, perovskite significantly outperforms silicon, particularly at detecting high-energy X-rays. This is a crucial advantage when it comes to monitoring X-rays at high-energy research facilities, such as synchrotron light sources.
Perovskite films can be deposited on surfaces by spraying solutions that cure and leave thin layers of the material behind As a result, the thin-layer detectors will be much easier and cheaper to produce than silicon-based detectors, which require high-temperature metal deposition under vacuum conditions.
"Potentially, we could use ink-jet types of systems to print large scale detectors," said Tsai. "This would allow us to replace half-million-dollar silicon detector arrays with inexpensive, higher-resolution perovskite alternatives."
In addition to the promise of thin-layer perovskites in X-ray detectors, thicker layers work well provided they include a small voltage source. This suggests that their useful energy range could be extended beyond X-rays to low-energy gamma-rays.
###
The new prototype was fabricated and tested successfully thanks to a collaborative effort among Los Alamos National Laboratory material scientists led by Wanyi Nie and Hsinhan Tsai, and the Los Alamos Theory team led by Sergei Tretiak, in conjunction with Joseph Strzalka at Argonne National Laboratory's X-ray Science Division.
####
About Los Alamos National Laboratory
Los Alamos National Laboratory, a multidisciplinary research institution engaged in strategic science on behalf of national security, is operated by Triad, a public service oriented, national security science organization equally owned by its three founding members: Battelle Memorial Institute (Battelle), the Texas A&M University System (TAMUS), and the Regents of the University of California (UC) for the Department of Energy's National Nuclear Security Administration.
Los Alamos enhances national security by ensuring the safety and reliability of the U.S. nuclear stockpile, developing technologies to reduce threats from weapons of mass destruction, and solving problems related to energy, environment, infrastructure, health, and global security concerns.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
James Riordon
505-551-4004
@LosAlamosNatLab
Copyright © Los Alamos National Laboratory
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Thin films
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
2 Dimensional Materials
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Perovskites
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Law enforcement/Anti-Counterfeiting/Security/Loss prevention
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








