Home > Press > Hair surface engineering to be advanced by nano vehicles: This new researched technology can help both drug delivery and hair cosmetics industry
 |
Abstract:
"Hair surface engineering: modification of fibrous materials of biological origin using functional ceramic nano containers", a project headed by Rawil Fakhrullin, is supported by the Russian Science Foundation.
Hair surface engineering to be advanced by nano vehicles: This new researched technology can help both drug delivery and hair cosmetics industry
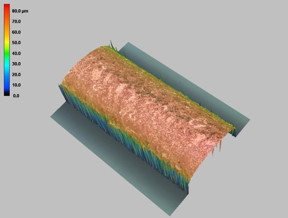
Kazan, Russian Federation | Posted on April 10th, 2020Dr. Fakhrullin explains, "We will modify the surface of hair and other fibrous materials of natural origin by the directed formation of nano-structured layers based on functional inorganic ceramic nano containers carrying a variety of organic components. Materials of natural origin are hypoallergenic, comfortable to use, but they have rather low wear resistance, and they are prone to deformation and biodegradation. Directed modification of properties using functionalized nano materials will significantly expand the field of application of natural fibers."
Based on the close similarity of the microstructure of fibrous materials of natural origin and mammalian hair, the scientists are going to create a universal technology for modifying the surface of fibers of biological origin for use in the textile and cosmetic industries.
«By modifying the fibrous structures of natural origin, it will be possible to change their aesthetic properties (color, texture and smell), protect them from biodegradation by applying antibacterial, fungicidal and insecticidal preparations, as well as increase the fire resistance of fabrics and non-woven materials based on wool, cotton, linen and silk,» elaborates Fakhrullin.
KFU bionanotechnologists will develop methods for modifying human hair. With their help, it will be possible not only to change the color of the hair, thickness, texture and aroma, but also to protect the structure of the hair and skin under them from ultraviolet radiation.
In addition, using these methods, the project head is convinced, it will be possible to create tools for applying topical anti-inflammatory drugs based on functional nano containers. When applied to human hair in affected areas of the skin, they will provide a prolonged gradual release of drugs. Veterinary preparations with a similar principle of action can be applied to the fur of farm and domestic animals for medicinal purposes.
In the process, scientists will also study the fundamental processes of self-assembly of inorganic nanoparticles on the surface of biological fibers and determine the optimal parameters for the directed modification of the properties of fibrous materials.
"Inorganic nano particles of various origin, biopolymers and their complexes will be used to study the patterns of self-assembly of nanoparticles on the surface of fibers," Fakhrullin concludes.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Yury Nurmeev
@KazanUni
Copyright © Kazan Federal University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Self Assembly
![]() Diamond glitter: A play of colors with artificial DNA crystals May 17th, 2024
Diamond glitter: A play of colors with artificial DNA crystals May 17th, 2024
![]() Liquid crystal templated chiral nanomaterials October 14th, 2022
Liquid crystal templated chiral nanomaterials October 14th, 2022
![]() Nanoclusters self-organize into centimeter-scale hierarchical assemblies April 22nd, 2022
Nanoclusters self-organize into centimeter-scale hierarchical assemblies April 22nd, 2022
![]() Atom by atom: building precise smaller nanoparticles with templates March 4th, 2022
Atom by atom: building precise smaller nanoparticles with templates March 4th, 2022
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Food/Agriculture/Supplements
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() SMART researchers pioneer first-of-its-kind nanosensor for real-time iron detection in plants February 28th, 2025
SMART researchers pioneer first-of-its-kind nanosensor for real-time iron detection in plants February 28th, 2025
![]() Silver nanoparticles: guaranteeing antimicrobial safe-tea November 17th, 2023
Silver nanoparticles: guaranteeing antimicrobial safe-tea November 17th, 2023
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








