Home > Press > A distinct spin on atomic transport: Work that demonstrates simultaneous control over transport and spin properties of cold atoms establishes a framework for exploring concepts of spintronics and solid-state physics
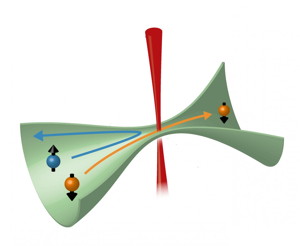 |
| An optical beam (red) introduces an effect equivalent to applying a magnetic field inside an optically defined structure in which the atoms move (green). Atoms in the energetically lower spin state (orange) can flow while atoms in a higher spin state (blue) are blocked. CREDIT (ETH Zurich/D-PHYS, adapted from doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.123.193605) |
Abstract:
One of the more unexpected things that can be done with charge-neutral atoms is to use them to emulate the fundamental behaviour of electrons. In the past few years, the group of Tilman Esslinger at the Institute of Quantum Electronics in the Department of Physics of ETH Zurich has pioneered a platform in which atoms cooled to temperatures close to absolute zero are transported through one- and two-dimensional structures, driven by a potential difference. In this way defining phenomena occuring in mesoscopic electronic systems can be studied in great detail, not least quantized conductance. In a pair of papers published today in Physical Review Letters and Physical Review A, postdoc Laura Corman, former PhD student Martin Lebrat and colleagues in the Esslinger group report that they have mastered in their transport experiments control over another quantum property of the atoms --- their spin.
A distinct spin on atomic transport: Work that demonstrates simultaneous control over transport and spin properties of cold atoms establishes a framework for exploring concepts of spintronics and solid-state physics
Zurich, Switzerland | Posted on November 8th, 2019The team added to the transport channel a tightly focussed light beam, which induces local interactions that are equivalent to exposing the atoms to a strong magnetic field. As a consequence, the degeneracy of the spin states is lifted, which in turn serves as the basis for an efficient spin filter: atoms of one spin orientation are repelled, whereas those of another orientation are free to pass (see the figure). Importantly, even though the application of an additional light field leads to the loss of atoms, these dissipative processes do not destroy the quantization of conductance. The ETH researchers replicate this experimental finding in numerical simulation and substantiate its validity through an extension of the Landauer--Büttiker model, the key formalism for quantum transport.
The efficiency of the atomic spin filter demonstrated by the Esslinger group matches that of the best equivalent elements for electronic systems. This, together with the extraordinary 'cleanness' and controllability of the cold-atom platform, opens up exciting new perspectives for exploring the dynamics of quantum transport. In particular, as the interaction between the atoms can be tuned, the platform provides access to spin transport of strongly correlated quantum systems. This regime is difficult to study otherwise, but is of considerable fundamental and practical interest, not least for applications in spintronic devices and to explore fundamental phases of matter.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Andreas Trabesinger
41-791-289-860
Copyright © ETH Zurich Department of Physics
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Quantum Physics
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Spintronics
![]() Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Quantum Computing
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Quantum nanoscience
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








