Home > Press > Breakthrough enables storage and release of mechanical waves without energy loss: The development may have broad implications for efficient harvesting, storing, and control of energy flow for mechanical and optical applications
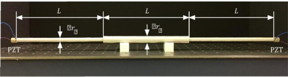 |
| Experimental setup, consisting of a waveguide bar with cavity and side channels. The excitation of elastic waves traveling along the bar is provided by piezoelectric actuators placed at the two ends of the system. Credit: Giuseppe Trainiti, Georgia Tech CREDIT Giuseppe Trainiti, Georgia Tech |
Abstract:
•Their proof-of-concept experiment may have broad implications for efficient harvesting, storing, and control of energy flow for mechanical and optical applications
The findings may facilitate improved technology for monitoring the structural integrity of bridges and other structural components
•The discovery may also lead to improved methods for energy harvesting and storage, wireless charging of electric vehicles, and may also have applications in quantum computing and ultralow-energy photonics
Breakthrough enables storage and release of mechanical waves without energy loss: The development may have broad implications for efficient harvesting, storing, and control of energy flow for mechanical and optical applications
New York, NY | Posted on August 30th, 2019Light and sound waves are at the basis of energy and signal transport and fundamental to some of our most basic technologies -- from cell phones to engines. Scientists, however, have yet to devise a method that allows them to store a wave intact for an indefinite period of time and then direct it toward a desired location on demand. Such a development would greatly facilitate the ability to manipulate waves for a variety of desired uses, including energy harvesting, quantum computing, structural-integrity monitoring, information storage, and more.
In a newly published paper in Science Advances, a group of researchers led by Andrea Alù, founding director of the Photonics Initiative at the Advanced Science Research Center (ASRC) at The Graduate Center, CUNY, and by Massimo Ruzzene, professor of Aeronautics Engineering at Georgia Tech, have experimentally shown that it is possible to efficiently capture and store a wave intact then guide it towards a specific location.
"Our experiment proves that unconventional forms of excitation open new opportunities to gain control over wave propagation and scattering," said Alù. "By carefully tailoring the time dependence of the excitation, it is possible to trick the wave to be efficiently stored in a cavity, and then release it on demand towards the desired direction."
Methodology
To achieve their goal, the scientists had to devise a way for changing the basic interaction between waves and materials. When a light or sound wave hits an obstacle, it is either partially absorbed or reflected and scattered. The absorption process entails immediately converting of the wave into heat or other forms of energy. Materials that can't absorb waves only reflect and scatter them. The researchers' goal was to find a way to mimic the absorbtion process without converting the wave into other forms of energy and instead storing it in the material. This concept, introduced theoretically two years ago by the ASRC group, is known as coherent virtual absorption.
To prove their theory, the researchers reasoned that they needed to tailor the waves' time evolution so that when they came in contact with non-abosorbing materials, they wouldn't be reflected, scattered, or transmitted. This would prevent the wave impinging on the structure from escaping, and it would be efficiently trapped inside as if it were being absorbed. The stored wave could then be released on demand.
During their experiment, researchers propagated two mechanical waves traveling in opposite directions along a carbon steel waveguide bar that contained a cavity. The time variations of each wave were carefully controlled to ensure that the cavity would retain all of the impinging energy. Then, by stopping the excitation or detuning one of the waves, they were able to control the release of the stored energy and send it towards a desired direction on demand.
"While we ran our proof-of-concept experiment using elastic waves traveling in a solid material, our findings are also applicable to radiowaves and light, offering exciting prospects for efficient energy harvesting, wireless power transfer, low-energy photonics, and generally enhanced control over wave propagation," said Ruzzene.
###
Research Funding
This study was funded by the the Air Force Office of Scientific Research, the National Science Foundation, and the Simons Foundation.
####
About Advanced Science Research Center, GC/CUNY
The Advanced Science Research Center (ASRC) at The Graduate Center, CUNY is a world-leading center of scientific excellence, which elevates scientific research and education at CUNY and beyond through initiatives in five distinctive, but broadly interconnected disciplines: nanoscience, photonics, neuroscience, structural biology, and environmental sciences. The ASRC promotes a collaborative, interdisciplinary research culture where renowned scientists advance their discoveries using state-of-the-art equipment and cutting-edge core facilities.
About The Graduate Center of The City University of New York
The Graduate Center, CUNY is a leader in public graduate education devoted to enhancing the public good through pioneering research, serious learning, and reasoned debate. The Graduate Center offers ambitious students more than 40 doctoral and master's programs of the highest caliber, taught by top faculty from throughout CUNY -- the nation's largest public urban university. Through its nearly 40 centers, institutes, initiatives, and the Advanced Science Research Center, The Graduate Center influences public policy and discourse and shapes innovation. The Graduate Center's extensive public programs make it a home for culture and conversation.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Shawn Rhea
212-817-7180
Copyright © Advanced Science Research Center, GC/CUNY
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Quantum Computing
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Optical computing/Photonic computing
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
![]() Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
![]() Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
Construction
![]() Temperature-sensing building material changes color to save energy January 27th, 2023
Temperature-sensing building material changes color to save energy January 27th, 2023
![]() Strain-sensing smart skin ready to deploy: Nanotube-embedded coating detects threats from wear and tear in large structures July 15th, 2022
Strain-sensing smart skin ready to deploy: Nanotube-embedded coating detects threats from wear and tear in large structures July 15th, 2022
![]() A sunlight-driven “self-healing” anti-corrosion coating May 27th, 2022
A sunlight-driven “self-healing” anti-corrosion coating May 27th, 2022
![]() Polymer fibers with graphene nanotubes make it possible to heat hard-to-reach, complex-shaped items February 11th, 2022
Polymer fibers with graphene nanotubes make it possible to heat hard-to-reach, complex-shaped items February 11th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








