Home > Press > Direct radiolabeling of nanomaterials: Directly radiolabeled nanographene materials without chelators are suitable for bioimaging applications
 |
| © Wiley-VCH |
Abstract:
Positron emission tomography plays a pivotal role for monitoring the distribution and accumulation of radiolabeled nanomaterials in living subjects. The radioactive metals are usually connected to the nanomaterial through an anchor, a so-called chelator, but this chemical binding can be omitted if nanographene is used, as American scientists report in the journal Angewandte Chemie. The replacement of chelator-based labeling by intrinsic labeling significantly enhances the bioimaging accuracy and reduces biases.
Direct radiolabeling of nanomaterials: Directly radiolabeled nanographene materials without chelators are suitable for bioimaging applications
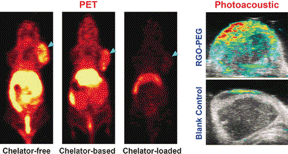
Hoboken, NJ | Posted on February 9th, 2017Nanoparticles are very promising substances for biodiagnostics (e.g., detecting cancerous tissue) and biotherapy (e.g., destroying tumors by molecular agents), because they are not as fast metabolized as normal pharmaceuticals and they particularly enrich in tumors through an effect called enhanced permeability and retention (EPR). Chelators, which have a macrocyclic structure, are used to anchor the radioactive element (e.g., copper-64) onto the nanoparticles' surface. The tracers are then detected and localized in the body with the help of a positron emission tomography (PET) scanner. However, the use of a chelator can also be problematic, because it can detach from the nanoparticles or bias the imaging. Therefore, the group of Weibo Cai at University of Wisconsin-Madison, USA, sought for chelator-free solutions--and found it in nanographene, one of the most promising substances in nanotechnology.
Nanographene offers the electronic system to provide special binding electrons for some transition metal ions. "π bonds of nanographene are able to provide the additional electron to stably incorporate the (64)Cu(2+) acceptor ions onto the surface of graphene," the authors wrote. Thus, it was possible to directly and stably attach the copper isotope to reduced graphene oxide nanomaterials stabilized by poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG), and this system was used for several bioimaging tests including the detection of tumors in mice.
After injection in the mouse model, the scientists observed long blood circulation and high tumor uptake. "Prolonged blood circulation of (64)Cu-RGO-PEG [...] induced a prompt and persistent tumor uptake via EPR effect," they wrote. Moreover, the directly radiolabeled nanographene was readily prepared by simply mixing both components and heating them. This simple chelator-free, intrinsically labeled system may provide an attractive alternative to the chelator-based radiolabeling, which is still the "gold standard" in bioimaging.
###
About the Author
Dr. Cai is an Associate Professor with joint appointment in the Departments of Radiology and Medical Physics at the University of Wisconsin-Madison, USA. His laboratory's research projects are focused on molecular imaging, molecular therapy, and nanotechnology. Dr. Cai has received many awards for his research.
mi.wisc.edu/
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Mario Mueller
Copyright © Wiley
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








