Home > Press > Prototype device for measuring graphene-based electromagnetic radiation created: Russian scientists have created a prototype device for measuring graphene-based electromagnetic radiation
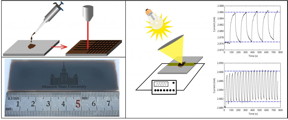 |
| This is a schematic of the structuring of graphene oxide: Photo microstructuring; Prototype circuit of the bolometer and its work. CREDIT Stanislav Evlashin |
Abstract:
Bolometer is a device for measuring electromagnetic radiation energy flow based on measurement of variations of physical parameters of thermosensitive element as a result of heating by absorption of radiation energy.
Prototype device for measuring graphene-based electromagnetic radiation created: Russian scientists have created a prototype device for measuring graphene-based electromagnetic radiation
Moscow, Russia | Posted on November 1st, 2016"We studied thermal and optical properties of the carbon structures derived from the reduced graphene oxide in a wide range of wavelengths from visible to infrared. In addition to the optical and thermal properties of the carbon structures, we have demonstrated the bolometer prototype that operates at room temperature without additional cooling", says Stanislav Evlashin, the first author of the article, the researcher of the Skobeltsyn Institute of Nuclear Physics Lomonosov Moscow State University (SINP MSU), PhD in Physico-Mathematical Sciences.
Synthesis and investigations of the new materials for bolometric sensors have a great scientific and practical importance. Such materials should possess a high effective absorption over a wide spectral range, high stable thermoresistive effect (change in electrical conductance with temperature), and, of course, they must be cheap to manufacture.
To create bolometer prototype the water solution of graphene oxide was used, which was obtained by the standard method of graphite oxidation, which is known and widely used. The resulting suspension of graphene oxide was deposited on the substrate for subsequent laser microstructuring. Laser treatment causes partial reduction of graphene oxide film and changes morphology, consequently, it changes optical and thermal properties of graphene oxide.
The material synthesis and development of the bolometer prototype was held at SINP MSU. Studies on the optical properties were carried out at Physics Department of Moscow State University. Research on the thermal properties were carried out at LPI RAS.
"Laser microstructuring of graphene oxide opens up the possibility of selective creation of antireflective, thermally-conductive and electrically-conductive coatings. Developed method is quite cheap, compatible with conventional semiconductor technology and allows you to create antiabsorbing coatings that would cover large areas on almost any surface. The observed properties of reduced graphene oxide partially show the prospects of it's use in bolometric matrices and other IR devices," - says Stanislav Evlashin.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Vladimir Koryagin
Copyright © Lomonosov Moscow State University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








