Home > Press > Lithium-ion batteries: Capacity might be increased by 6 times
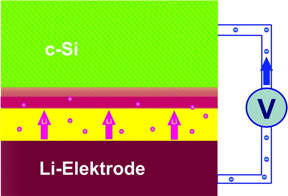 |
| Lithium ions migrate through the electrolyte (yellow) into the layer of crystalline silicon (c-Si). During the charging cycle, a 20-nm layer (red) develops on the silicon electrode adsorbing extreme quantities of lithium atoms. CREDIT: HZB |
Abstract:
The team was able to show through neutron measurements made at the Institut Laue-Langevin in Grenoble, France, that lithium ions do not penetrate deeply into the silicon. During the charge cycle, a 20-nm anode layer develops containing an extremely high proportion of lithium. This means extremely thin layers of silicon would be sufficient to achieve the maximal load of lithium.
Lithium-ion batteries: Capacity might be increased by 6 times
Berlin, Germany | Posted on August 9th, 2016Lithium-ion batteries provide laptops, smart phones, and tablet computers with reliable energy. However, electric vehicles have not gotten as far along with conventional lithium-ion batteries. This is due to currently utilised electrode materials such as graphite only being able to stably adsorb a limited number of lithium ions, restricting the capacity of these batteries. Semiconductor materials like silicon are therefore receiving attention as alternative electrodes for lithium batteries. Bulk silicon is able to absorb enormous quantities of lithium. However, the migration of the lithium ions destroys the crystal structure of silicon. This can swell the volume by a factor of three, which leads to major mechanical stresses.
Observation during charging cycle
Now a team from the HZB Institute for Soft Matter and Functional Materials headed by Prof. Matthias Ballauff has directly observed for the first time a lithium-silicon half-cell during its charging and discharge cycles. "We were able to precisely track where the lithium ions adsorb in the silicon electrode using neutron reflectometry methods, and also how fast they were moving", comments Dr. Beatrix-Kamelia Seidlhofer, who carried out the experiments using the neutron source located at the Institute Laue-Langevin.
Lithium-rich layer of only 20 nanometer
She discovered two different zones during her investigations. Near the boundary to the electrolytes, a roughly 20-nm layer formed having extremely high lithium content: 25 lithium atoms were lodged among 10 silicon atoms. A second adjacent layer contained only one lithium atom for ten silicon atoms. Both layers together are less than 100 nm thick after the second charging cycle.
Theoretical maximum capacity
After discharge, about one lithium ion per silicon node in the electrode remained in the silicon boundary layer exposed to the electrolytes. Seidlhofer calculates from this that the theoretical maximum capacity of these types of silicon-lithium batteries lies at about 2300 mAh/g. This is more than six times the theoretical maximum attainable capacity for a lithium-ion battery constructed with graphite (372 mAh/g).
Less is more
These are substantial findings that could improve the design of silicon electrodes: very thin silicon films should be sufficient for adsorbing the maximum possible amount of lithium, which in turn would save on material and especially on energy consumed during manufacture - less is more!
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Dr. Beatrix-K. Seidlhofer
49-308-062-114-026
Copyright © Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin für Materialien und Energie
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








