Home > Press > Electronic device detects molecules linked to cancer, Alzheimer's and Parkinson's: An inexpensive portable biosensor has been developed by researchers at Brazil's National Nanotechnology Laboratory with FAPESP's support
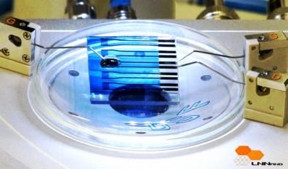 |
| An inexpensive portable biosensor has been developed by researchers at Brazil's National Nanotechnology Laboratory with FAPESP's support. CREDIT: LNNano |
Abstract:
A biosensor developed by researchers at the National Nanotechnology Laboratory (LNNano) in Campinas, São Paulo State, Brazil, has been proven capable of detecting molecules associated with neurodegenerative diseases and some types of cancer.
Electronic device detects molecules linked to cancer, Alzheimer's and Parkinson's: An inexpensive portable biosensor has been developed by researchers at Brazil's National Nanotechnology Laboratory with FAPESP's support
São Paulo, Brasil | Posted on May 20th, 2016The device is basically a single-layer organic nanometer-scale transistor on a glass slide. It contains the reduced form of the peptide glutathione (GSH), which reacts in a specific way when it comes into contact with the enzyme glutathione S-transferase (GST), linked to Parkinson's, Alzheimer's and breast cancer, among other diseases. The GSH-GST reaction is detected by the transistor, which can be used for diagnostic purposes.
The project focuses on the development of point-of-care devices by researchers in a range of knowledge areas, using functional materials to produce simple sensors and microfluidic systems for rapid diagnosis.
"Platforms like this one can be deployed to diagnose complex diseases quickly, safely and relatively cheaply, using nanometer-scale systems to identify molecules of interest in the material analyzed," explained Carlos Cesar Bof Bufon, Head of LNNano's Functional Devices & Systems Lab (DSF) and a member of the research team for the project, whose principal investigator is Lauro Kubota, a professor at the University of Campinas's Chemistry Institute (IQ-UNICAMP).
In addition to portability and low cost, the advantages of the nanometric biosensor include its sensitivity in detecting molecules, according to Bufon.
"This is the first time organic transistor technology has been used in detecting the pair GSH-GST, which is important in diagnosing degenerative diseases, for example," he explained. "The device can detect such molecules even when they're present at very low levels in the examined material, thanks to its nanometric sensitivity." A nanometer (nm) is one billionth of a meter (10-9 meter), or one millionth of a millimeter.
The system can be adapted to detect other substances, such as molecules linked to different diseases and elements present in contaminated material, among other applications. This requires replacing the molecules in the sensor with others that react with the chemicals targeted by the test, which are known as analytes.
The team is working on paper-based biosensors to lower the cost even further and to improve portability and facilitate fabrication as well as disposal.
The challenge is that paper is an insulator in its usual form. Bufon has developed a technique to make paper conductive and capable of transporting sensing data by impregnating cellulose fibers with polymers that have conductive properties.
The technique is based on in situ synthesis of conductive polymers. For the polymers not to remain trapped on the surface of the paper, they have to be synthesized inside and between the pores of the cellulose fibers. This is done by gas-phase chemical polymerization: a liquid oxidant is infiltrated into the paper, which is then exposed to monomers in the gas phase. A monomer is a molecule of low molecular weight capable of reacting with identical or different molecules of low molecular weight to form a polymer.
The monomers evaporate under the paper and penetrate the pores of the fibers at the submicrometer scale. Inside the pores, they blend with the oxidant and begin the polymerization process right there, impregnating the entire material.
The polymerized paper acquires the conductive properties of the polymers. This conductivity can be adjusted by manipulating the element embedded in the cellulose fibers, depending on the application for which the paper is designed. Thus, the device can be electrically conductive, allowing current to flow without significant losses, or semiconductive, interacting with specific molecules and functioning as a physical, chemical or electrochemical sensor.
####
About FAPESP
FAPESP (www.fapesp.br/en) is a public foundation, funded by the taxpayer in the State of São Paulo, with the mission to support research projects in higher education and research institutions, in all fields of knowledge. São Paulo has a population of forty million and generates 35% of Brazil’s GNP. The constitution of the State establishes that 1% of all state taxes belong to the foundation and the government transfers these funds monthly. The stability of the funding and the autonomy of the foundation allow for an efficient management of the resources that has had a sizable impact: while São Paulo has 22% of the Brazilian population and 30% of the scientists with a doctorate in the country, the state responds for 52% of the country’s scientific articles published in international journals.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Samuel Antenor
55-113-838-4381
Copyright © FAPESP
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Cancer
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








