Home > Press > Electrochemical etching down to one-monolayer towards high-Tc superconductivity: A new route for exploration of nontrivial physical phenomena at two-dimensional materials
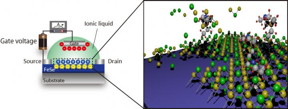 |
| (Left) Device structure of electric-double-layer transistor with FeSe channel deposited on oxide substrate. (Right) One-monolayer FeSe is realized by electrochemical etching where Fe and Se ions are dissolved into ionic liquid. CREDIT: Junichi Shiogai |
Abstract:
Iron selenide (FeSe) is an attracting superconducting material since the superconducting transition temperature (Tc) is enhanced from 8 K in bulk form toward 65 K in one-monolayer form.
Electrochemical etching down to one-monolayer towards high-Tc superconductivity: A new route for exploration of nontrivial physical phenomena at two-dimensional materials
Sendai, Japan | Posted on November 4th, 2015However, systematic thickness dependence of electrical measurement has been difficult to address.
A team of researchers at Tohoku University's Institute for Materials Research (IMR), has realized layer-by-layer etching in superconducting FeSe films down to approximately one-monolayer about 0.6 nm using classical electrochemical reaction in electric-double-layer transistor configuration.
As the thickness of the films becomes thin, the superconducting transition temperature (Tc) is increased from bulk value (8 K) to about 40 K. In addition, the research group unveils that by combining with an electrostatic charging effect, the high-Tc transition can be induced in 10-nm thick condition (20 monolayers), which had been limited in one/two-monolayers so far.
The development of this etching technique will pave the way for the exploration of nontrivial physical phenomena in atomically thin two-dimensional films. This had previously been difficult to address by conventional methods.
This work was published in Nature Physics online on Nov 2, 2015.
###
Publication Information
Authors: J. Shiogai, Y. Ito, T. Mitsuhashi, T. Nojima and A. Tsukazaki
Title: Electric-field-induced superconductivity in electrochemically etched ultrathin FeSe films on SrTiO3 and MgO
Journal: Nature Physics
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Junichi Shiogai
Copyright © Tohoku University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Thin films
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Superconductivity
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








