Home > Press > Dielectric film has refractive index close to air
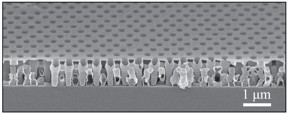 |
| By manipulating the structure of aluminum oxide, a dielectric material, researchers were able to improve its optical and mechanical properties. The key to the film's performance is the highly-ordered spacing of the pores, which gives it a more mechanically robust structure without impairing the refractive index. You can see the structure here, on the micrometer scale. CREDIT: Chih-Hao Chang |
Abstract:
“Ordered Three-Dimensional Thin-Shell Nanolattice Materials with Near-Unity Refractive Indices”
Authors: Xu A. Zhang, Abhijeet Bagal, Erinn C. Dandley, Junjie Zhao, Chrisopher J. Oldham, Gregory N. Parsons and Chih-Hao Chang, North Carolina State University; Bae-Ian Wu, Air Force Research Laboratory
Published: Oct. 12, Advanced Functional Materials
DOI: 10.1002/adfm.201502854
Abstract: The refractive indices of naturally occurring materials are limited, and there exists an index gap between indices of air and available solid materials. With many photonics and electronics applications, there has been considerable effort in creating artificial materials with optical and dielectric properties similar to air while simultaneously being mechanically stable to bear load. Here we demonstrate a class of ordered nanolattice materials consisting of periodic thin-shell structures with near-unity refractive index and high stiffness. Using a combination of three-dimensional nanolithography and atomic layer deposition, these ordered nanostructured material have reduced optical scattering and improved mechanical stability compared to existing randomly porous materials. Using ZnO and Al2O3 as the building materials, refractive indices from 1.3 down to 1.025 were achieved. The experimental data can be accurately described by Maxwell-Garnett effective media theory, which can provide a guide for index design. The demonstrated low-index, low-scattering, and high-stiffness materials can serve as high-quality optical films in multilayer photonic structures, waveguides, resonators, and ultra-low-k dielectrics.
Dielectric film has refractive index close to air
Raleigh, NC | Posted on October 12th, 2015Researchers from North Carolina State University have developed a dielectric film that has optical and electrical properties similar to air, but is strong enough to be incorporated into electronic and photonic devices - making them both more efficient and more mechanically stable.
At issue is something called refractive index, which measures how much light bends when it moves through a substance. Air, for example, has a refractive index of 1, while water has a refractive index of 1.33 - which is why a straw appears to bend when you put it in a glass of water.
Photonic devices require a high contrast between its component materials, with some components having a high refractive index and others have a low one. The higher the contrast between those materials, the more efficient the photonic device is - and the better it performs. Air has the lowest refractive index, but it isn't mechanically stable. And the lowest refractive index found in solid, naturally occurring materials is 1.39.
But now researchers have developed a film made of aluminum oxide that has a refractive index as low as 1.025 but that is mechanically stiff.
"By manipulating the structure of the aluminum oxide, which is dielectric, we've improved both its optical and mechanical properties," says Chih-Hao Chang, corresponding author of a paper on the work and an assistant professor of mechanical and aerospace engineering at NC State. Dielectrics are insulator materials that are used in an enormous array of consumer products. For example, every handheld device has hundreds of capacitors, which are dielectric components that can store and manage electric charge.
"The key to the film's performance is the highly-ordered spacing of the pores, which gives it a more mechanically robust structure without impairing the refractive index," says Xu Zhang, lead author of the paper and a Ph.D. student at NC State.
The researchers make the film by first using a nanolithography developed in Chang's lab to create highly-ordered pores in a polymer substrate. That porous polymer then serves as a template, which the researchers coats with a thin layer of aluminum oxide using atomic layer deposition. The polymer is then burned off, leaving behind a three-dimensional aluminum oxide coating.
"We are able to control the thickness of the aluminum oxide, creating a coating between two nanometers and 20 nanometers thick," Zhang says. "Using zinc oxide in the same process, we can create a thicker coating. And the thickness of the coating controls and allows us to design the refractive index of the film." Regardless of the how thick the coating is, the film itself is approximately one micrometer thick.
"The steps in the process are potentially scalable, and are compatible with existing chip manufacturing processes," Chang says. "Our next steps include integrating these materials into functional optical and electronic devices."
###
The paper, "Ordered Three-Dimensional Thin-Shell Nanolattice Materials with Near-Unity Refractive Indices," is published online in the journal Advanced Functional Materials. The paper was co-authored by Abhijeet Bagal, Erinn Dandley, Junjie Zhao, Chrisopher Oldham and Gregory Parsons of NC State; and by Bae-Ian Wu of the Air Force Research Laboratory.
The work was done with support from the Air Force Research Laboratory and from NASA under grant NNX12AQ46G.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Matt Shipman
919-515-6386
Copyright © North Carolina State University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Thin films
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Optical computing/Photonic computing
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
![]() Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
![]() Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Aerospace/Space
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








