Home > Press > SLAC's ultrafast 'electron camera' visualizes ripples in 2-D material: Understanding motions of thin layers may help design solar cells, electronics and catalysts of the future
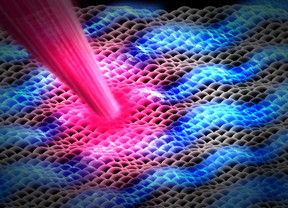 |
| Researchers have used SLAC's experiment for ultrafast electron diffraction (UED), one of the world's fastest 'electron cameras' to take snapshots of a three-atom-thick layer of a promising material as it wrinkles in response to a laser pulse. Understanding these dynamic ripples could provide crucial clues for the development of next-generation solar cells, electronics and catalysts.
CREDIT: SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory |
Abstract:
New research led by scientists from the Department of Energy's SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory and Stanford University shows how individual atoms move in trillionths of a second to form wrinkles on a three-atom-thick material. Revealed by a brand new "electron camera," one of the world's speediest, this unprecedented level of detail could guide researchers in the development of efficient solar cells, fast and flexible electronics and high-performance chemical catalysts.
SLAC's ultrafast 'electron camera' visualizes ripples in 2-D material: Understanding motions of thin layers may help design solar cells, electronics and catalysts of the future
Menlo Park, CA | Posted on September 10th, 2015The breakthrough, accepted for publication Aug. 31 in Nano Letters, could take materials science to a whole new level. It was made possible with SLAC's instrument for ultrafast electron diffraction (UED), which uses energetic electrons to take snapshots of atoms and molecules on timescales as fast as 100 quadrillionths of a second.
"This is the first published scientific result with our new instrument," said scientist Xijie Wang, SLAC's UED team lead. "It showcases the method's outstanding combination of atomic resolution, speed and sensitivity."
SLAC Director Chi-Chang Kao said, "Together with complementary data from SLAC's X-ray laser Linac Coherent Light Source, UED creates unprecedented opportunities for ultrafast science in a broad range of disciplines, from materials science to chemistry to the biosciences." LCLS is a DOE Office of Science User Facility.
Extraordinary Material Properties in Two Dimensions
Monolayers, or 2-D materials, contain just a single layer of molecules. In this form they can take on new and exciting properties such as superior mechanical strength and an extraordinary ability to conduct electricity and heat. But how do these monolayers acquire their unique characteristics? Until now, researchers only had a limited view of the underlying mechanisms.
"The functionality of 2-D materials critically depends on how their atoms move," said SLAC and Stanford researcher Aaron Lindenberg, who led the research team. "However, no one has ever been able to study these motions on the atomic level and in real time before. Our results are an important step toward engineering next-generation devices from single-layer materials." The research team looked at molybdenum disulfide, or MoS2, which is widely used as a lubricant but takes on a number of interesting behaviors when in single-layer form - more than 150,000 times thinner than a human hair.
For example, the monolayer form is normally an insulator, but when stretched, it can become electrically conductive. This switching behavior could be used in thin, flexible electronics and to encode information in data storage devices. Thin films of MoS2 are also under study as possible catalysts that facilitate chemical reactions. In addition, they capture light very efficiently and could be used in future solar cells.
Because of this strong interaction with light, researchers also think they may be able to manipulate the material's properties with light pulses.
"To engineer future devices, control them with light and create new properties through systematic modifications, we first need to understand the structural transformations of monolayers on the atomic level," said Stanford researcher Ehren Mannebach, the study's lead author.
Electron Camera Reveals Ultrafast Motions
Previous analyses showed that single layers of molybdenum disulfide have a wrinkled surface. However, these studies only provided a static picture. The new study reveals for the first time how surface ripples form and evolve in response to laser light.
Researchers at SLAC placed their monolayer samples, which were prepared by Linyou Cao's group at North Carolina State University, into a beam of very energetic electrons. The electrons, which come bundled in ultrashort pulses, scatter off the sample's atoms and produce a signal on a detector that scientists use to determine where atoms are located in the monolayer. This technique is called ultrafast electron diffraction.
The team then used ultrashort laser pulses to excite motions in the material, which cause the scattering pattern to change over time.
"Combined with theoretical calculations, these data show how the light pulses generate wrinkles that have large amplitudes - more than 15 percent of the layer's thickness - and develop extremely quickly, in about a trillionth of a second. This is the first time someone has visualized these ultrafast atomic motions," Lindenberg said.
Once scientists better understand monolayers of different materials, they could begin putting them together and engineer mixed materials with completely new optical, mechanical, electronic and chemical properties.
###
The research was supported by DOE's Office of Science, the SLAC UED/UEM program development fund, the German National Academy of Sciences, and the U.S. National Science Foundation.
Citation: E. M. Mannebach et al., Nano Letters, 31 August 2015 (10.1021/acs.nanolett.5b02805)
####
About SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory
SLAC is a multi-program laboratory exploring frontier questions in photon science, astrophysics, particle physics and accelerator research. Located in Menlo Park, California, SLAC is operated by Stanford University for the U.S. Department of Energy Office of Science. To learn more, please visit www.slac.stanford.edu.
SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory is supported by the Office of Science of the U.S. Department of Energy. The Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States, and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit science.energy.gov.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Andrew Gordon
650-926-2282
Copyright © SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Chemistry
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Single-atom catalysts change spin state when boosted by a magnetic field June 4th, 2025
Single-atom catalysts change spin state when boosted by a magnetic field June 4th, 2025
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Flexible Electronics
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








