Home > Press > Down to the quantum dot: Jülich researchers develop ultrahigh-resolution 3-D microscopy technique for electric fields
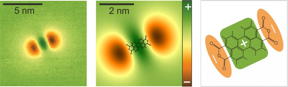 |
| Left: The scanning quantum dot micrograph of a PTCDA molecule reveals the negative partial charges at the ends of the molecule as well as the positive partial charges in the center. Center: Simulated electric potential above a PTCDA molecule with molecular structure. Right: Schematic of charge distribution in the PTCDA molecule. CREDIT: Copyright: Forschungszentrum Juelich |
Abstract:
Using a single molecule as a sensor, scientists in Jülich have successfully imaged electric potential fields with unrivalled precision. The ultrahigh-resolution images provide information on the distribution of charges in the electron shells of single molecules and even atoms. The 3D technique is also contact-free. The first results achieved using "scanning quantum dot microscopy" have been published in the current issue of Physical Review Letters. The related publication was chosen as the Editor's suggestion and selected as a Viewpoint in the science portal Physics. The technique is relevant for diverse scientific fields including investigations into biomolecules and semiconductor materials.
Down to the quantum dot: Jülich researchers develop ultrahigh-resolution 3-D microscopy technique for electric fields
Jülich, Germany | Posted on July 7th, 2015"Our method is the first to image electric fields near the surface of a sample quantitatively with atomic precision on the sub-nanometre scale," says Dr. Ruslan Temirov from Forschungszentrum Jülich. Such electric fields surround all nanostructures like an aura. Their properties provide information, for instance, on the distribution of charges in atoms or molecules.
For their measurements, the Jülich researchers used an atomic force microscope. This functions a bit like a record player: a tip moves across the sample and pieces together a complete image of the surface. To image electric fields up until now, scientists have used the entire front part of the scanning tip as a Kelvin probe. But the large size difference between the tip and the sample causes resolution difficulties - if we were to imagine that a single atom was the same size as a head of a pin, then the tip of the microscope would be as large as the Empire State Building.
Single molecule as a sensor
In order to improve resolution and sensitivity, the scientists in Jülich attached a single molecule as a quantum dot to the tip of the microscope. Quantum dots are tiny structures, measuring no more than a few nanometres across, which due to quantum confinement can only assume certain, discrete states comparable to the energy level of a single atom.
The molecule at the tip of the microscope functions like a beam balance, which tilts to one side or the other. A shift in one direction or the other corresponds to the presence or absence of an additional electron, which either jumps from the tip to the molecule or does not. The "molecular" balance does not compare weights but rather two electric fields that act on the mobile electron of the molecular sensor: the first is the field of a nanostructure being measured, and the second is a field surrounding the tip of the microscope, which carries a voltage.
"The voltage at the tip is varied until equilibrium is achieved. If we know what voltage has been applied, we can determine the field of the sample at the position of the molecule," explains Dr. Christian Wagner, a member of Temirov's Young Investigators group at Jülich's Peter Grünberg Institute (PGI-3). "Because the whole molecular balance is so small, comprising only 38 atoms, we can create a very sharp image of the electric field of the sample. It's a bit like a camera with very small pixels."
Universally applicable
A patent is pending for the method, which is particularly suitable for measuring rough surfaces, for example those of semiconductor structures for electronic devices or folded biomolecules. "In contrast to many other forms of scanning probe microscopy, scanning quantum dot microscopy can even work at a distance of several nanometres. In the nanoworld, this is quite a considerable distance," says Christian Wagner. Until now, the technique developed in Jülich has only been applied in high vacuum and at low temperatures: essential prerequisites to carefully attach the single molecule to the tip of the microscope.
"In principle, variations that would work at room temperature are conceivable," believes the physicist. Other forms of quantum dots could be used as a sensor in place of the molecule, such as those that can be realized with semiconductor materials: one example would be quantum dots made of nanocrystals like those already being used in fundamental research.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Tobias Schloesser
49-246-161-4771
Copyright © Forschungszentrum Juelich
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Quantum Dots/Rods
![]() A new kind of magnetism November 17th, 2023
A new kind of magnetism November 17th, 2023
![]() IOP Publishing celebrates World Quantum Day with the announcement of a special quantum collection and the winners of two prestigious quantum awards April 14th, 2023
IOP Publishing celebrates World Quantum Day with the announcement of a special quantum collection and the winners of two prestigious quantum awards April 14th, 2023
![]() Qubits on strong stimulants: Researchers find ways to improve the storage time of quantum information in a spin rich material January 27th, 2023
Qubits on strong stimulants: Researchers find ways to improve the storage time of quantum information in a spin rich material January 27th, 2023
![]() NIST’s grid of quantum islands could reveal secrets for powerful technologies November 18th, 2022
NIST’s grid of quantum islands could reveal secrets for powerful technologies November 18th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








