Home > Press > NIST’s grid of quantum islands could reveal secrets for powerful technologies
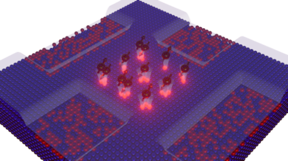 |
| Researchers created a grid of quantum dots (center) ranging from one to three phosphorus atoms deposited onto a plane embedded in silicon and studied the properties of electrons injected into the grid. CREDIT Wang et al./NIST |
Abstract:
Researchers at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) have created grids of tiny clumps of atoms known as quantum dots and studied what happens when electrons dive into these archipelagos of atomic islands. Measuring the behavior of electrons in these relatively simple setups promises deep insights into how electrons behave in complex real-world materials and could help researchers engineer devices that make possible powerful quantum computers and other innovative technologies.
NIST’s grid of quantum islands could reveal secrets for powerful technologies
Gaithersburg, MD | Posted on November 18th, 2022In work published in Nature Communications, the researchers made multiple 3-by-3 grids of precisely spaced quantum dots, each comprising one to three phosphorus atoms. Attached to the grids were electrical leads and other components that enabled electrons to flow through them. The grids provided playing fields in which electrons could behave in nearly ideal, textbook-like conditions, free of the confounding effects of real-world materials.
The researchers injected electrons into the grids and observed how they behaved as the researchers varied conditions such as the spacing between the dots. For grids in which the dots were close, the electrons tended to spread out and act like waves, essentially existing in several places at one time. When the dots were far apart, they would sometimes get trapped in individual dots, like electrons in materials with insulating properties.
Advanced versions of the grid would allow researchers to study the behavior of electrons in controllable environments with a level of detail that would be impossible for the world’s most powerful conventional computers to simulate accurately. It would open the door to full-fledged “analog quantum simulators” that unlock the secrets of exotic materials such as high-temperature superconductors. It could also provide hints about how to create materials, such as topological insulators, by controlling the geometry of the quantum dot array.
In related work just published in ACS Nano, the same NIST researchers improved their fabrication method so they can now reliably create an array of identical, equally spaced dots with exactly one atom each, leading to even more ideal environments necessary for a fully accurate quantum simulator. The researchers have set their sights on making such a simulator with a larger grid of quantum dots: A 5x5 array of dots can produce rich electron behavior that is impossible to simulate in even the most advanced supercomputers.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Ben Stein
National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)
Office: 301-209-3097
Copyright © National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Quantum Physics
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
2 Dimensional Materials
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Quantum Computing
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Quantum Dots/Rods
![]() A new kind of magnetism November 17th, 2023
A new kind of magnetism November 17th, 2023
![]() IOP Publishing celebrates World Quantum Day with the announcement of a special quantum collection and the winners of two prestigious quantum awards April 14th, 2023
IOP Publishing celebrates World Quantum Day with the announcement of a special quantum collection and the winners of two prestigious quantum awards April 14th, 2023
![]() Qubits on strong stimulants: Researchers find ways to improve the storage time of quantum information in a spin rich material January 27th, 2023
Qubits on strong stimulants: Researchers find ways to improve the storage time of quantum information in a spin rich material January 27th, 2023
![]() Lattice distortion of perovskite quantum dots induces coherent quantum beating September 9th, 2022
Lattice distortion of perovskite quantum dots induces coherent quantum beating September 9th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








