Home > Press > Handheld scanner could make brain tumor removal more complete, reducing recurrence
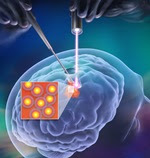 |
| A handheld device that resembles a laser pointer could someday help surgeons remove all of the cells in a brain tumor. Credit: Moritz Kircher |
Abstract:
Cancerous brain tumors are notorious for growing back despite surgical attempts to remove them — and for leading to a dire prognosis for patients. But scientists are developing a new way to try to root out malignant cells during surgery so fewer or none get left behind to form new tumors. The method, reported in the journal ACS Nano, could someday vastly improve the outlook for patients.
Handheld scanner could make brain tumor removal more complete, reducing recurrence
Washington, DC | Posted on September 3rd, 2014Moritz F. Kircher and colleagues at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center point out that malignant brain tumors, particularly the kind known as glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), are among the toughest to beat. Although relatively rare, GBM is highly aggressive, and its cells multiply rapidly. Surgical removal is one of the main weapons doctors have to treat brain tumors. The problem is that currently, there's no way to know if they have taken out all of the cancerous cells. And removing extra material "just in case" isn't a good option in the brain, which controls so many critical processes. The techniques surgeons have at their disposal today are not accurate enough to identify all the cells that need to be excised. So Kircher's team decided to develop a new method to fill that gap.
The researchers used a handheld device resembling a laser pointer that can detect "Raman nanoprobes" with very high accuracy. These nanoprobes are injected the day prior to the operation and go specifically to tumor cells, and not to normal brain cells. Using a handheld Raman scanner in a mouse model that mimics human GBM, the researchers successfully identified and removed all malignant cells in the rodents' brains. Also, because the technique involves steps that have already made it to human testing for other purposes, the researchers conclude that it has the potential to move readily into clinical trials. Surgeons might be able to use the device in the future to treat other types of brain cancer, they say.
###
The authors acknowledge funding from the National Institutes of Health.
####
About American Chemical Society
The American Chemical Society is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. With more than 161,000 members, ACS is the world's largest scientific society and a global leader in providing access to chemistry-related research through its multiple databases, peer-reviewed journals and scientific conferences. Its main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Michael Bernstein
202-872-6042
Moritz F. Kircher, M.D., Ph.D.
Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center
New York, NY 10065
Copyright © American Chemical Society
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Alliances/Trade associations/Partnerships/Distributorships
![]() Chicago Quantum Exchange welcomes six new partners highlighting quantum technology solutions, from Chicago and beyond September 23rd, 2022
Chicago Quantum Exchange welcomes six new partners highlighting quantum technology solutions, from Chicago and beyond September 23rd, 2022
![]() University of Illinois Chicago joins Brookhaven Lab's Quantum Center June 10th, 2022
University of Illinois Chicago joins Brookhaven Lab's Quantum Center June 10th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








