Home > Press > Copper shines as flexible conductor
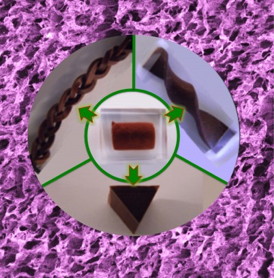 |
| Sensors made with copper are cheap, light, flexible and highly conductive. |
Abstract:
Bend them, stretch them, twist them, fold them: modern materials that are light, flexible and highly conductive have extraordinary technological potential, whether as artificial skin or electronic paper.
Copper shines as flexible conductor
Victoria, Australia | Posted on August 29th, 2014Making such concepts affordable enough for general use remains a challenge but a new way of working with copper nanowires and a PVA "nano glue" could be a game-changer.
Previous success in the field of ultra-lightweight "aerogel monoliths" has largely relied on the use of precious gold and silver nanowires.
By turning instead to copper, both abundant and cheap, researchers at Monash University and the Melbourne Centre for Nanofabrication have developed a way of making flexible conductors cost-effective enough for commercial application.
"Aerogel monoliths are like kitchen sponges but ours are made of ultra fine copper nanowires, using a fabrication process called freeze drying," said lead researcher Associate Professor Wenlong Cheng, from Monash University's Department of Chemical Engineering.
"The copper aerogel monoliths are conductive and could be further embedded into polymeric elastomers - extremely flexible, stretchable materials - to obtain conducting rubbers."
Despite its conductivity, copper's tendency to oxidation and the poor mechanical stability of copper nanowire aerogel monoliths mean its potential has been largely unexplored.
The researchers found that adding a trace amount of poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) to their aerogels substantially improved their mechanical strength and robustness without impairing their conductivity.
What's more, once the PVA was included, the aerogels could be used to make electrically conductive rubber materials without the need for any prewiring. Reshaping was also easy.
"The conducting rubbers could be shaped in arbitrary 1D, 2D and 3D shapes simply by cutting, while maintaining the conductivities," Associate Professor Cheng said.
The versatility extends to the degree of conductivity. "The conductivity can be tuned simply by adjusting the loading of copper nanowires," he said. "A low loading of nano wires would be appropriate for a pressure sensor whereas a high loading is suitable for a stretchable conductor."
Affordable versions of these materials open up the potential for use in a range of new-generation concepts: from prosthetic skin to electronic paper, for implantable medical devices, and for flexible displays and touch screens.
They can be used in rubber-like electronic devices that, unlike paper-like electronic devices, can stretch as well as bend. They can also be attached to topologically complex curved surfaces, serving as real skin-like sensing devices, Associate Professor Cheng said.
In their report, published recently in ACS Nano, the researchers noted that devices using their copper-based aerogels were not quite as sensitive as those using gold nanowires, but had many other advantages, most notably their low-cost materials, simpler and more affordable processing, and great versatility.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Glynis Smalley
61-408-027-848
Copyright © Monash University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Flexible Electronics
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() Flexible electronics integrated with paper-thin structure for use in space January 17th, 2025
Flexible electronics integrated with paper-thin structure for use in space January 17th, 2025
Display technology/LEDs/SS Lighting/OLEDs
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








