Home > Press > A review article summarizes the state-of-the-art knowledge about graphene grain boundaries
 |
Abstract:
The graphene produced by chemical vapor deposition is typically polycrystalline. Authors from the ICN2 Theoretical and Computational Nanoscience Group, led by ICREA Research professor Stephan Roche, together with authors from Sungkyunkwan University, analyse in Advanced Materials the challenges and opportunities of these structures.
A review article summarizes the state-of-the-art knowledge about graphene grain boundaries
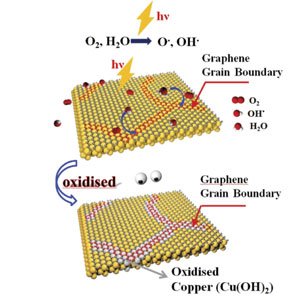
Barcelona, Spain | Posted on July 11th, 2014Graphene has attracted significant interest both for exploring fundamental science and for a wide range of technological applications. Chemical vapor deposition (CVD) is currently the only working approach to grow graphene at big scale, which is required for industrial applications. Unfortunately, the produced graphene is typically polycrystalline, consisting of a patchwork of grains with various orientations and sizes, joined by grain boundaries of irregular shapes.
Researchers from the Institut Catalŕ de Nanocičncia i Nanotecnologia (ICN2) Theoretical and Computational Nanoscience Group curated a review article in Advanced Materials to determine whether graphene grain boundaries are a blessing or a curse. ICREA Research Professor Stephan Roche, Group Leader at ICN2, together with Dr Aron Cummings, Jose Eduardo Barrios Vargas and Van Tuan Dinh, from the same Group, share the authorship of the review with researchers from Sungkyunkwan University. The review article not only provides guidelines for the improvement of graphene devices, but also opens a new research area of engineering graphene grain boundaries for highly sensitive electro-biochemical devices.
The review analyses the challenges and opportunities of charge transport in polycrystalline graphene, which means summarizing the state-of-the-art knowledge about graphene grain boundaries (GGBs). The review is divided in the following sections: Structure and Morphology of GGBs; Methods of Observing GGBs; Measurement of Electrical Transport across GGBs; Manipulation of GGBs with Functional Groups.
The work describes how TEM and STM, combined with theory and simulation, can provide information for the observation and characterization of GGBs at the atomic scale. These boundaries have interesting properties, such as the fact that they can be a good template for the synthesis of 1D materials, might be useful to design sensors for detecting gases and molecules or allow selective diffusion of limited gases and molecules. Controlling the atomic structure of GGBs by CVD is a big challenge from a scientific point of view, but would be a huge step forward in the realization of next-generation technologies based on this material.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Ŕlex Argemí, ICN2 Marketing and Communication Manager
Phone: 937372607
Fax: 937372607
Copyright © ICN2
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








