Home > Press > Layered security: Carbon nanotubes promise improved flame-resistant coating
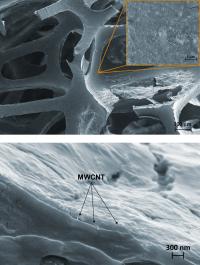 |
| An easy-to-apply, NIST-developed coating significantly reduces the flammability of foam used in furniture. The thin coating is deposited onto the surface of all the nooks and crannies of the porous foam (top), with heat-dissipating multiwalled carbon nanotubes uniformly distributed throughout (bottom). (Color added for clarity.)
Credit: Kim/NIST |
Abstract:
Using an approach akin to assembling a club sandwich at the nanoscale, National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) researchers have succeeded in crafting a uniform, multi-walled carbon-nanotube-based coating that greatly reduces the flammability of foam commonly used in upholstered furniture and other soft furnishings.
Layered security: Carbon nanotubes promise improved flame-resistant coating
Gaithersburg, MD | Posted on January 15th, 2014he flammability of the nanotube-coated polyurethane foam was reduced 35 percent compared with untreated foam. As important, the coating prevented melting and pooling of the foam, which generates additional flames that are a major contributor to the spread of fires.
Nationwide, fires in which upholstered furniture is the first item ignited account for about 6,700 home fires annually and result in 480 civilian deaths, or almost 20 percent of home fire deaths between 2006 and 2010, according to the National Fire Protection Association.
The innovative NIST technique squeezes nanotubes between two everyday polymers and stacks four of these trilayers on top of each other. The result is a plastic-like coating that is thinner than one-hundredth the diameter of human hair and has flame-inhibiting nanotubes distributed evenly throughout.
The brainchild of NIST materials scientists Yeon Seok Kim and Rick Davis, the fabrication method is described in the January 2014 issue of Thin Solid Films.* Kim and Davis write that the technique can be used with a variety of types of nanoparticles to improve the quality of surface coatings for diverse applications.
The pair experimented with a variety of layer-by-layer coating methods before arriving at their triple-decker approach. All had failed to meet their three key objectives: entire coverage of the foam's porous surface, uniform distribution of the nanotubes, and the practicality of the method. Inmost of these trials, the nanotubes—cylinders of carbon atoms resembling rolls of chicken wire—did not adhere strongly to the foam surface.
So, Kim and Davis opted to doctor the nanotubes themselves, borrowing a technique often used in cell culture to make DNA molecules stickier. The method attached nitrogen-containing molecules—called amine groups—to the nanotube exteriors.
This step proved critical: The doctored nanotubes were uniformly distributed and clung tenaciously to the polymer layers above and below. As a result, the coating fully exploits the nanotubes' rapid heat-dissipating capability.
Gram for gram, the resulting coating confers much greater resistance to ignition and burning than achieved with the brominated flame retardants commonly used to treat soft furnishings today. As important, says Davis, a "protective char layer" forms when the nanotube-coated foam is exposed to extreme heat, creating a barrier that prevents the formation of melt pools.
"This kind of technology has the potential to reduce the fire threat associated with burning soft furniture in homes by about a third," Davis says.
###
*Y.S. Kim and R. Davis. Multi-walled carbon nanotube layer-by-layer coatings with a trilayer structure to reduce foam flammability. Thin Solid Films 550 (2014) 184-189.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Mark Bello
301-975-3776
Copyright © National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings/Nanosheets
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Home
![]() Nanomaterials enable dual-mode heating and cooling device: Device could cut HVAC energy use by nearly 20% in the US December 2nd, 2020
Nanomaterials enable dual-mode heating and cooling device: Device could cut HVAC energy use by nearly 20% in the US December 2nd, 2020
![]() Bosch Sensortec launches ideation community to foster and accelerate innovative IoT applications : Creativity hub for customers, partners, developers and makers February 18th, 2019
Bosch Sensortec launches ideation community to foster and accelerate innovative IoT applications : Creativity hub for customers, partners, developers and makers February 18th, 2019
![]() Iran Develops Water-Repellent Nano-Paint December 5th, 2018
Iran Develops Water-Repellent Nano-Paint December 5th, 2018
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








