Home > Press > Low-power tunneling transistor for high-performance devices at low voltage
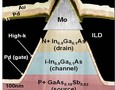 |
| Transmission electron microscope cross-section of the vertical TFET. The interface of the source and channel is the point where electron tunneling occurs. ILD is the interlayer dielectric separating the contacts. Top plane contacts are Gold (Au), Palladium (Pd), and Molybdenum (Mo). Image: Suman Datta/Penn State |
Abstract:
A new type of transistor that could make possible fast and low-power computing devices for energy-constrained applications such as smart sensor networks, implantable medical electronics and ultra-mobile computing is feasible, according to Penn State researchers. Called a near broken-gap tunnel field effect transistor (TFET), the new device uses the quantum mechanical tunneling of electrons through an ultrathin energy barrier to provide high current at low voltage.
Low-power tunneling transistor for high-performance devices at low voltage
Washington, DC | Posted on December 12th, 2013Penn State, the National Institute of Standards and Technology and IQE, a specialty wafer manufacturer, jointly presented their findings at the International Electron Devices Meeting in Washington, D.C. The IEDM meeting includes representatives from all of the major chip companies and is the recognized forum for reporting breakthroughs in semiconductor and electronic technologies.
Tunnel field effect transistors are considered to be a potential replacement for current CMOS transistors, as device makers search for a way to continue shrinking the size of transistors and packing more transistors into a given area. The main challenge facing current chip technology is that as size decreases, the power required to operate transistors does not decrease in step. The results can be seen in batteries that drain faster and increasing heat dissipation that can damage delicate electronic circuits. Various new types of transistor architecture using materials other than the standard silicon are being studied to overcome the power consumption challenge.
"This transistor has previously been developed in our lab to replace MOSFET transistors for logic applications and to address power issues," said lead author and Penn State graduate student Bijesh Rajamohanan. "In this work we went a step beyond and showed the capability of operating at high frequency, which is handy for applications where power concerns are critical, such as processing and transmitting information from devices implanted inside the human body."
For implanted devices, generating too much power and heat can damage the tissue that is being monitored, while draining the battery requires frequent replacement surgery. The researchers, led by Suman Datta, professor of electrical engineering, tuned the material composition of the indium gallium arsenide/gallium arsenide antimony so that the energy barrier was close to zero -- or near broken gap, which allowed electrons to tunnel through the barrier when desired. To improve amplification, the researchers moved all the contacts to the same plane at the top surface of the vertical transistor.
This device was developed as part of a larger program sponsored by the National Science Foundation through the Nanosystems Engineering Research Center for Advanced Self-Powered Systems of Integrated Sensors and Technologies (NERC-ASSIST). The broader goal of the ASSIST program is to develop battery-free, body-powered wearable health monitoring systems with Penn State, North Carolina State University, University of Virginia, and Florida International University as participating institutions.
The paper, "Demonstration of InGaAs/GaAsSb Near Broken-gap Tunnel FET with Ion=740µA/µm, GM=700µS/µm and Gigahertz Switching Performance at VDS=0.5V," will be available in the conference proceedings publication of the IEDM.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Walt Mills
(814) 865-0285
A'ndrea Elyse Messer
(814) 865-9481
Dr. Datta
Mr. Rajamohanan
Copyright © Penn State
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Quantum nanoscience
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








