Home > Press > Organic electronics -- how to make contact between carbon compounds and metal
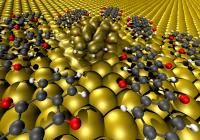 |
| Upon contact between the oxygen atoms protruding from the backbone and the metal, the molecules' internal structure changed in such a way that they lost their semiconducting properties and instead adopted the metallic properties of the surface.
Credit: Visualisation: Georg Heimel/HU Berlin |
Abstract:
Until now, however, it was practically impossible to accurately predict which molecules performed well on the job. They basically had to be identified by trial-and-error.
Now, an international team of scientists around Dr. Georg Heimel and Prof. Norbert Koch from the HZB and the Humboldt University Berlin has unraveled the mystery of what these molecules have in common. Their discovery enables more focused improvements to contact layers between metal electrodes and active materials in organic electronic devices.
Organic electronics -- how to make contact between carbon compounds and metal
Berlin, Germany | Posted on February 18th, 2013"We have been working on this question for a number of years now and could at last come up with a conclusive picture using a combination of several experimental methods and theoretical calculations," Georg Heimel explains. The researchers systematically examined different types of molecules whose backbones consist of the same chain of fused aromatic carbon rings. They differed in just one little detail: the number of oxygen atoms projecting from the backbone. These modified molecules were placed on the typical contact metals gold, silver, and copper.
Using photoelectron spectroscopy (UPS and XPS) at HZB's own BESSY II synchrotron radiation source, the researchers were able to identify chemical bonds that formed between the metal surfaces and the molecules as well as to measure the energy levels of the conduction electrons. Colleagues from Germany's Tübingen University determined the exact distance between the molecules and the metal surfaces using x-ray standing wave measurements taken at the ESRF synchrotron radiation source in Grenoble, France.
These experiments showed that, upon contact between the oxygen atoms protruding from the backbone and several of the metals, the molecules' internal structure changed in such a way that they lost their semiconducting properties and instead adopted the metallic properties of the surface. Despite similar prerequisites, this effect was not observed for the "bare"-backbone molecule. From the observation which molecules underwent these kinds of drastic changes on what metal, the researchers could derive general guidelines. "At this point, we have a pretty good sense of how molecules ought to look like and what their properties should be if they are to be good mediators between active organic materials and metal contacts, or, as we like to call it, good at forming soft metallic contacts," says Heimel.
Experts from a number of other German universities and from research facilities in Suzhou (China), Iwate and Chiba (Japan), and ESRF (France) have also contributed substantially to this publication.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Dr. Georg Heimel
Prof. Dr. Norbert Koch
Fon: +49 30-20 93 78 19
Copyright © Helmholtz Association of German Research Centres
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Display technology/LEDs/SS Lighting/OLEDs
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








