Home > Press > Scientist Create New Nanoassembly Tech for Creating Complex Micro Structures for Use in Diagnostic Devices, Sensors & Other Apps
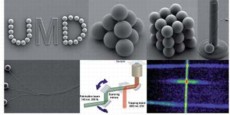 |
| Fourkas, et al article in Chemical Science,Volume 3, Number 8, August 2012, Pages 2449-2456. Image by Chemical Science |
Abstract:
University of Maryland Chemistry Professor John Fourkas and his research group have developed new materials and nanofabrication techniques for building miniaturized versions of components needed for medical diagnostics, sensors and other applications. These miniaturized components -- many impossible to make with conventional techniques -- would allow for rapid analysis at lower cost and with small sample volumes.
Scientist Create New Nanoassembly Tech for Creating Complex Micro Structures for Use in Diagnostic Devices, Sensors & Other Apps
College Park, MD | Posted on July 12th, 2012Fourkas and his team have created materials that allow the simultaneous 3D manipulation of microscopic objects using optical tweezers and a unique point-by-point method for lithography (the process of using light in etching silicon or other substrates to create chips and other electronic components).
As they report in a research article published in the August issue of Chemical Science , the combination of these techniques allows them to assemble complex 3D structures from multiple microscopic components.
This work builds on earlier breakthroughs by Fourkas and his team in the use of visible light for making tiny structures for applications such as optical communications, controlling cell behavior and manufacturing integrated circuits.
"These materials have opened the door to a suite of new techniques for micro and nanofabrication," says Fourkas. "For instance, we have been able to perform braiding and weaving with threads that have a diameter that is more than 100 times smaller than that of a human hair." In the paper, Fourkas and his group also showcase 3D structures composed of glass microspheres, a microscopic tetherball pole, and a microscopic needle eye that has been threaded.
"One of the exciting aspects of this set of techniques is that it is compatible with a wide range of materials. For instance, we can weave together threads with completely different compositions to create functional microfabrics or build microscopic devices `brick by brick with building blocks that have different chemical or physical properties."
In addition to being enabling technologies for the creation of microscopic analytical and diagnostic devices, Fourkas foresees these techniques being valuable in the study and control of the behavior of individual cells and groups of cells.
Simultaneous microscale optical manipulation, fabrication and immobilisation in aqueous media was authored by Farah Dawood, Sijia Qin, Linjie Li, Emily Y. Lin and John T. Fourkas.
The authors acknowledge the support of the UMD and National Science Foundation (NSF)-supported Materials Research Science & Engineering Center
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Lee Tune
301 405 4679
Copyright © University of Maryland
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() To learn more about research in the Fourkas laboratories, visit:
To learn more about research in the Fourkas laboratories, visit:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Printing/Lithography/Inkjet/Inks/Bio-printing/Dyes
![]() Presenting: Ultrasound-based printing of 3D materials—potentially inside the body December 8th, 2023
Presenting: Ultrasound-based printing of 3D materials—potentially inside the body December 8th, 2023
![]() Simple ballpoint pen can write custom LEDs August 11th, 2023
Simple ballpoint pen can write custom LEDs August 11th, 2023
![]() Disposable electronics on a simple sheet of paper October 7th, 2022
Disposable electronics on a simple sheet of paper October 7th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








